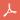
What is CRISPR/Cas9 delivery system
DIAGNOSTIC ANTIBODY & ANTIGEN
SERVICES
- Custom AAV Production
- Custom Adenovirus Production
- Custom Lentivirus Production
- Pre-made AAV Production
- Pre-made Adenovirus Production
- Pre-made Lentivirus Production
- AAV-LC3 Autophagy Flux Detection
- Ad-LC3 Autophagy Flux Detection
- Lv-LC3 Autophagy Flux Detection
- AAV Control Virus Production
- CRISPR/Cas9 AAV Production
- CRISPR/Cas9 Adenovirus Production
Gene editing, also called genome editing, is a group of technologies to change the sequence of DNA in the genome. Several approaches to genome editing have been developed, including Zinc Finger, TALEN, and CRISPR/Cas9. Compared with the other gene editing tools, CRISPR/Cas9 system is faster, cheaper, more accurate, and more efficient, showing unprecedented advantages in gene therapy.
CRISPR/Cas9 premade products
Cat No. | Products Name | Type of Crispr | Viral vector | Promoter | Fluorescent/Resistance | Tag | Order
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Ad-CMV-spCas9 |
spCas9 |
Adenovirus |
CMV |
zsgreen |
FLAG |
||
Adv-CMV-spCas9-zsgreen |
spCas9 |
Adenovirus |
CMV |
EGFP |
FLAG |
||
Adv-CMV-spCas9-EGFP |
spCas9 |
Adenovirus |
CMV |
Null |
FLAG |
||
Adv-CMV-spCas9-mcherry |
spCas9 |
Adenovirus |
CMV |
mcherry |
FLAG |
||
spCas9 |
lentivirus |
CMV |
puromycin |
FLAG |
|||
spCas9 |
lentivirus |
CMV |
zsgreen |
FLAG |
|||
spCas9 |
lentivirus |
CMV |
EGFP |
FLAG |
|||
spCas9 |
lentivirus |
CMV |
mcherry |
FLAG |
|||
spCas9 |
lentivirus |
CBH |
puromycin |
FLAG |
|||
spCas9 |
lentivirus |
CBH |
zsgreen |
FLAG |
CRISPR/Cas9 system can be delivered in vitro by the non-viral reagents (such as polymer, liposome, nano-particle, electroporation) or viral vectors (such as lentivirus, adenovirus and AAV) and in vivo by adenovirus or AAV vectors.
1)In vitro non-viral vectors CRISPR-Cas9 delivery system
In vitro non-viral vectors CRISPR/Cas9 delivery system can be mediated by non-viral reagents, such as polymer [51], liposome [52], nano-particle [53], electroporation [54]. The characteristics of these methods are summarized in the following table 2. For more detailed information about the transfection reagents, you can refer to the website: www.genemedi.com/i/transfection-in-vitro-in-vivo.
|
Table 2 – Comparison between polymer, liposome, nano-particle. |
||||
| Comparison | polymer | liposome | nano-particle | electroporation |
| Principle | endocytosis | endocytosis | membrane fusion/impale cells | transient increase in the permeability of cell membrane |
| Integration | No | No | No | No |
| Time to peak expression | 48h-72h | 48h-72h | 24h-48h | 48h-72h |
| Sutainable time | transient expression | transient expression | transient expression | transient expression |
| Cell Type | a number of cell types | adherent and suspension cell lines | Almost all the cells | not suitable for sensitive cell types |
| Particle diametre | 75 to 520 nm | 50-200nm | 100-300nm | —— |
| Animal experiment | low effiency | low effiency | target delivery | target delivery |
| Cytotoxicity | high | low | non-toxic | —— |
| Immune Response | No | No | No | No |
| Efficiency | low effiency (<10%) | depend on cell type | high efficiency | high efficiency |
| Price | inexpensive | medium | expensive | most expensive (electroporation device) |
2) In intro viral vectors CRISPR-Cas9 delivery system
a. lentiviral
With the ability to mediate efficient transfection and long-term expression of exogenous genes in both dividing and non-dividing cells, lentiviral is a good vector to deliver CRISPR system [55,56]. More useful information of lentivirus can be found on this website: www.genemedi.com/i/lentivirus-packaging.
b. adenoviral
Based on human adenovirus type 5 (Ad5), recombinant adenovirus (Ad) a replication-defective adenoviral vector system, is widely used for CRISPR-Cas9 system in most cell types [57-59]. Genemedi got a rich experience in adenovirus packaging, you could find more information on www.genemedi.com/i/adenovirus-packaging.
3) In vivo CRISPR-Cas9 delivery system-AAV-SaCas9
With mild immunogenicity, adeno-associated viruses (AAV) have superior biosafety rating and broad range of infectivity and mediate long-term and stable expression of CRISPR system in vivo. Considering the loading capacity of AAV (4.7kb), SaCas9 variant has been identified, referred to as KKH SaCas9, displaying robust genome editing activities at target sites with NNNRRT PAMs and showing comparable off-target effects between wild-type and KKH SaCas9 [60]. Combining CRISPR/SaCas9 system and AAV vector, AAV-SaCas9 has been widely applied for gene editing in vivo [61-63]. Genemedi is good at AAV production, please find more information on this website: www.genemedi.com/i/aav-packaging.
|
Table 3 – Comparison between Retrovirus, Lentivirus, Adenovirus and AAV vectors. |
||||
| Comparison | Retrovirus | Lentivirus | Adenovirus | AAV |
| Genome | ss RNA | ss RNA | ds DNA | ss DNA |
| Integration | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Packaging Capacity | 3kb | 4kb | 5.5kb | 2kb |
| Time to peak expression | 72h | 72h | 36h-72h | cell: 7 days; animals: 2 weeks |
| Sutainable time | about 3 weeks | stable expression | transient expression | > 6 months |
| Cell Type | Most Dividing | Most Dividing/Non-Dividing Cells | Most Dividing/Non-Dividing Cells | Most Dividing/Non-Dividing Cells |
| Titeration | 10^7 TU/ml | 10^8 TU/ml | 10^11 PFU/ml | 10^12 v.g./ml |
| Animal experiment | suitable | low efficiency | lowest efficiency | most suitable |
| Immune Response | high | medium | medium | ultra–low |