This briefing provides an update on previous briefings up to 11 March 2021
Summary
• There are 4 variants of concern and 6 variants under investigation (Table 1).
Definitions for variants of concern, variants under investigation and signals in monitoring
have been updated.
VOC-20DEC-01 (B.1.1.7) remains predominant. Other variants of concern and variants
under investigation remain a very low proportion of the available sequence data.
Mutation prevalence data show a decrease in the proportion of sequences with N439K
over time and an increase in E484K.
Enhanced investigations including secondary attack rates, spatial risk mapping, and
growth rates of each variant are provided for the first time. Numbers of all variants under
investigation remain low and estimates have low certainty.
An updated clinical risk assessment for VOC-20DEC-02 (B.1.351) is provided.
Variant information
The collection page gives content on variants, including prior technical briefings.
Updated definition for variants of concern, variants under
investigation and signals in monitoring
Updated case definitions have been applied as of 29 March 2021.
Variant of concern
Variant demonstrated to be associated with:
• an increase in transmissibility or other detrimental change in epidemiology,
and/or
• an increase in virulence or change in clinical disease presentation, and/or
• escape from immunity derived from natural infection, and/or
• a decrease in effectiveness of public health or clinical countermeasures
including:
o vaccination
o treatment in current clinical use
o testing if the impact is such that it is not easily mitigated by standard
laboratory quality and regulatory measures
Variant under investigation
Variant demonstrated to be associated with:
• variant with mutations for which there is high confidence predictive data, or
laboratory data, supporting significant adverse phenotypic change, but which
do not meet the definition of a variant of concern and
• evidence of community transmission in the UK or abroad
Signal in monitoring
Signals arise from horizon scanning and may be placed in monitoring if they do not meet
the definition of a VUI or VOC but are considered worth further investigation. Examples of
signals which are placed in monitoring:
• up to 5 importations to the UK with the same mutations associated with adverse
phenotypic change, but no evidence of UK or international community
transmission (for example, a single household, imports only)
or
• lineage with apparently high growth rate or prevalence in UK or abroad but with
no or inconclusive data on significance of mutations
or
• lineage where an international alert has been raised but data are incomplete
and further data are expected
or
• as designated by the Horizon Scanning Group
Single unusual genomes developing in individuals who are immunocompromised or have
prolonged shedding will not be monitored or escalated
unless there is evidence of
community transmission.
De-escalation
A variant of concern may be de-escalated if the evidence base changes so that it no
longer meets the phenotypic criteria, or if the affected countermeasure is no longer in use
or superseded (for example, an updated vaccine is available).
A variant under investigation may be de-escalated if laboratory or clinical data indicates
that it is unlikely to have the suspected phenotype (for example, if it contains mutations
containing for antigenic escape but laboratory data shows no reduced neutralisation
activity of convalescent and vaccinee sera).
Extinction
Either a variant of concern or variant under investigation will be considered provisionally
extinct if it has not been detected in any dataset for 12 weeks. Scanning of national and
international datasets will continue.
Variant status and numbers
Table 1 shows the current variants of concern and variants under investigation (including
new simplified naming convention as of 16 March 2021). Summary epidemiology on each
variant is shown in Table 2 (case numbers are also updated online Case numbers on
variants of concern (VOC) and variants under investigation (VUI).
Table 1. Variant lineage, designation and status as of 31 March 2021
| Lineage |
Prior designation (VOC/VUI) |
Designation as of 16 March 2021 |
First detected in sequence from |
Status |
| B.1.1.7 |
VOC 202012/01 |
VOC-20DEC01 |
UK |
VOC |
| B.1.351 |
VOC 202012/02 |
VOC-20DEC02 |
South Africa |
VOC |
| P1 |
VOC 202101/02 |
VOC-21JAN02 |
Japan ex Brazil |
VOC |
| B1.1.7 with E484K |
VOC 202102/02 |
VOC-21FEB02 |
UK |
VOC |
| P2 |
VUI 202101/01 |
VUI-21JAN-01 |
Brazil |
VUI |
| A.23.1 with E484K |
VUI 202102/01 |
VUI-21FEB-01 |
UK |
VUI |
| B.1.525 |
VUI 202102/03 |
VUI-21FEB-03 |
UK |
VUI |
| B.1.1.318 |
VUI 202102/04 |
VUI-21FEB-04 |
UK England |
VUI |
| B.1.324.1 with E484K |
VUI 202103/01 |
VUI-21MAR-01 |
UK |
VUI |
| P3 |
VUI 202103/02 |
VUI-21MAR-02 |
Philippines |
VUI |
| B.1.429 |
|
|
California USA |
Monitoring |
| B.1.1.7 with S494P |
|
|
UK |
Monitoring |
| A.27 |
|
|
France (Mayotte) |
Monitoring |
| B.1.526 |
|
|
New York USA |
Monitoring |
| B.1.1.7 with Q677H |
|
|
UK |
Monitoring |
| B.1 with E484Q and L452R |
|
|
India |
Monitoring |
| B.1 with E484K and S477N |
|
|
Under review |
Monitoring |
Variant prevalence
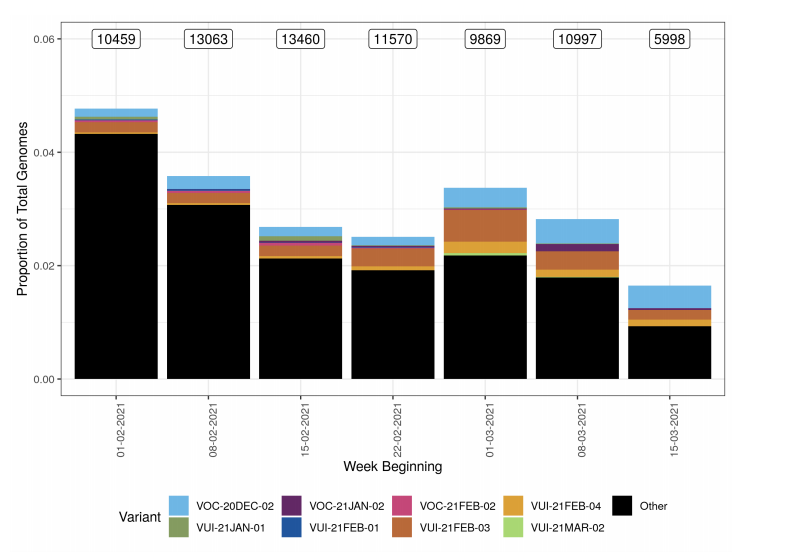
Variant prevalence for all available case data is presented in Figure 1 and Figure 2 that
show that the predominant variant at this time is VOC-20DEC-01 and other variants of
concern and under investigation represent a low proportion of available sequences. The
Other category in Figure 1 and Figure 2 includes genomes where the quality is insufficient
to determine variant status and genomes that do not meet the current definition for any
designated variant under investigation or variant of concern. The supplementary data for
figures is available here.
Figure 1. Variant prevalence for all England available case data from 1 February 2021 to 21 March 2021. (Find accessible data used in this graph in Variants of concern: technical briefing 8 – underlying data.)
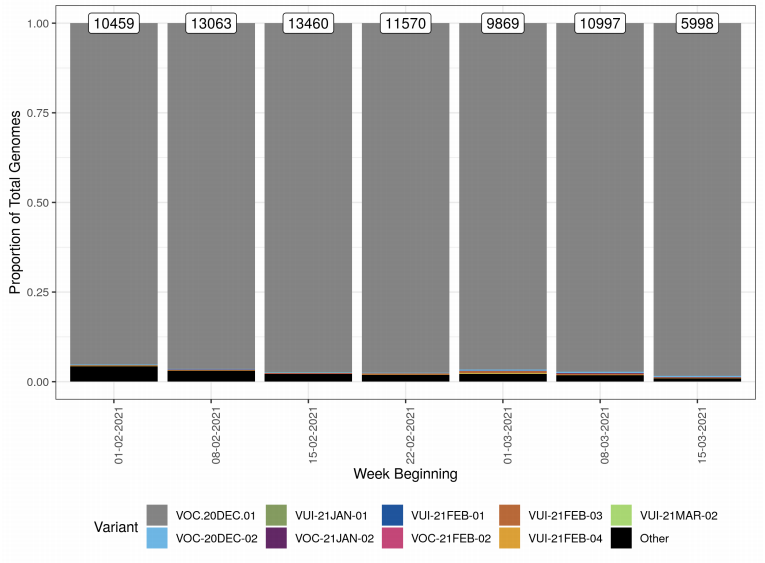 Figure 2. Variant prevalence for all England available case data from 1 February 2021 to 21 March 2021 excluding VOC20DEC-01.(Find accessible data used in this graph in Variants of concern: technical briefing 8 – underlying data.)
Figure 2. Variant prevalence for all England available case data from 1 February 2021 to 21 March 2021 excluding VOC20DEC-01.(Find accessible data used in this graph in Variants of concern: technical briefing 8 – underlying data.)
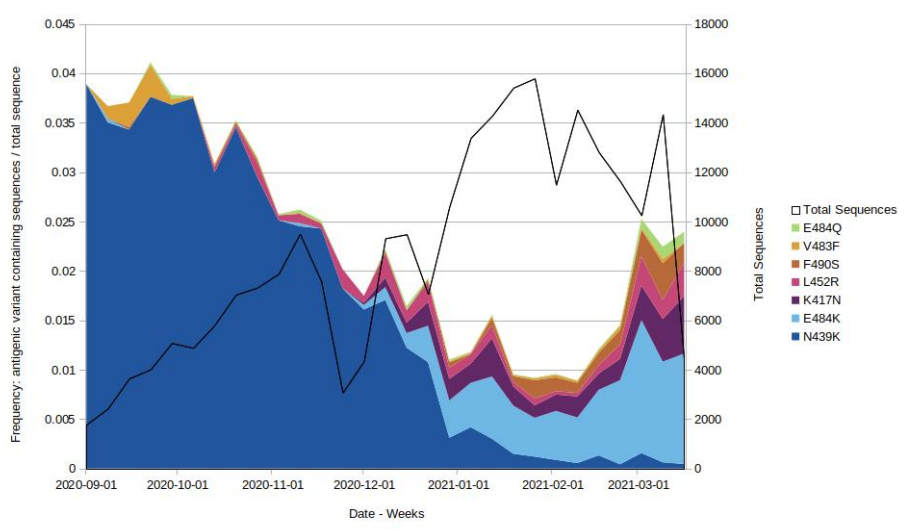
Antigenic change mutation monitoring
Mutations potentially associated with antigenic change are monitored as part of horizon
scanning. Figure 3 shows the proportion of these mutations over time in the all England
genomic dataset, illustrating the decline of N439K and an increase in E484K. Only those
mutations which were present at a count of > 50 within the 6 month time frame are shown.
The supplementary data for figures is available here.
Figure 3. Proportion of mutations conferring antigenic change over time from 1 September 2020 to 16 March 2021. (Find accessible data used in this graph in Variants of concern: technical briefing 8 – underlying data.)
Case numbers, proportion, deaths and case fatality rate
The number of cases of variants of concern and variant under investigation are shown in
Table 2, including the proportion of variant cases compared to all sequenced cases,
deaths and case fatality rate.
Table 2. Case number, proportion, death and case fatality rate of variants of concern and variant under investigation from 1 October 2020 to 31 March 2021
| Variant |
Case Numbera |
Case Proportionb |
Deathsc |
Case Fatality |
| VOC-20DEC-01 |
151,344 |
99.37% |
3,504 |
2.3% |
| VOC-20DEC-02 |
410 |
0.27% |
9 |
2.2% |
| VOC-21FEB-02 |
43 |
0.028% |
1 |
2.3% |
| VOC-21JAN-02 |
27 |
0.018% |
0 |
0.0% |
| VUI-21FEB-01 |
78 |
0.051% |
1 |
1.3% |
| VUI-21FEB-03 |
277 |
0.18% |
12 |
4.3% |
| VUI-21FEB-04 |
72 |
0.047% |
0 |
0.0% |
| VUI-21JAN-01 |
53 |
0.035% |
1 |
1.9% |
| VUI-21MAR-01 |
2 |
0.001% |
0 |
0.0% |
| VUI-21MAR-02 |
5 |
0.003% |
0 |
0.0% |
Excludes variant cases not linked to a known COVID-19 case. aCase number England genomic cases 31 March 2021. bProportion of sequences UK/England as of 31 March 2021. cDeaths As of 31 March 2021(within 28 days) with confirmed or probable VOC or total cases.
Enhanced investigations
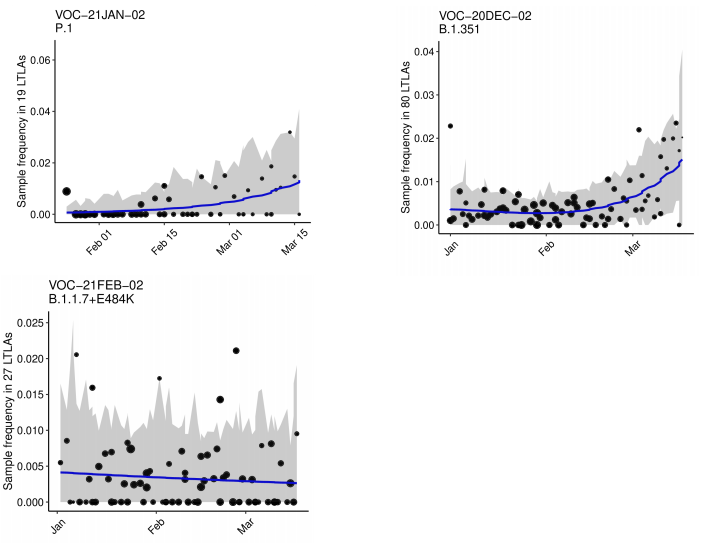
Growth rates
The growth rate estimates from a logistic growth model for variants of concern and
variants under investigation (with sufficient data) are shown in Table 3 and Figure 4 (for
those variants with sufficient cases). Growth rates are derived from pillar 2 (community
testing) data only which does not include targeted sequencing for travellers in quarantine.
Table 3 and Figure 4 show that the variants with significant positive growth rates
compared to other circulating lineages in the same area are VOC-20DEC-02 (B.1.351),
VOC-21JAN-02 (P.1), VUI-21FEB-03 (B.1.525) and VUI-21FEB-04 (B.1.1.318). The
supplementary data for figures is available here.
Table 3. Growth rate of variants of concern and variants under investigation 1 January 2021 as of 31 March 2021
| Variant |
Lineage |
Growthrate(1/week) |
| VOC-20DEC-02 |
B.1.351 |
0.16(p=7.59e-10) |
| VOC-21JAN-02 |
P.1 |
0.44(p=4.14e-05) |
| VOC-21FEB-02 |
B.1.1.7withE484K |
-0.092(p=0.047) |
| VUI-21JAN-01 |
P.2 |
-0.05(p=0.58) |
| VUI-21FEB-01 |
A.23.1withE484K |
0.11(p=0.21) |
| VUI-21FEB-03 |
B.1.525 |
0.34(p=1.97e-10) |
| VUI-21FEB-04 |
B.1.1.318 |
0.32(p=0.00025) |
Figure 4. Growth estimates of variants of concern and under investigation 1 January 2021 as of 31 March 2021. (Find accessible data used in this graph in Variants of concern: technical briefing 8 – underlying data.)
Secondary attack rates
Secondary attack rates are shown in Table 4. These are based on positive tests amongst
contacts named to NHS Test and Trace by an original case identified with a confirmed or
probable variant of concern or variant under investigation.
Secondary attack rates are shown for cases with and without travel history. In non-travel
settings, only close contacts (household members, face to face contact, people within 1
metre of the case for 1 minute or longer, or people within 2 metres for 15 minutes) named
by the original case are included. In travel settings the contacts reported are not restricted
to only close contacts named by the case (for example, they may include contacts on a
plane linked by additional contact tracing efforts), leading to likely deflation of secondary
attack rates amongst travellers compared to non-travellers. In addition, people recently
returning from overseas are subject to stricter quarantine measures and may moderate
their behaviour towards contacts. Travel history indicates, but does not confirm, where
infection of the original case occurred.
Secondary attack rates for contacts of non-travel cases with variants of concern or under
investigation except VOC-21FEB-02 are not significantly different from that for contacts of
non-travel cases with VOC-20DEC-01. No transmission events were identified to contacts
of cases with VOC-21FEB-02. Secondary attack rates for contacts of those that have
travelled with variants of concern or variants of interest were all considerably lower than
those that have not travelled.
Table 4. Case numbers and travel status including proportion and secondary attack rate for 5 January 2021 to 7 March
2021, data as of 29 March 2021
| Variant |
Lineage |
Cases in those that have travelled |
Cases in cases that have not travelled or unknown |
Case proportion have travelled |
Secondary Attack Rate among contacts of those that have travelled (95% CI) [secondary cases/contacts] |
Secondary Attack Rate amongs contacts of cases that have not travelled or unknown (95% CI) [secondary cases/contacts] |
| VOC-20DEC01 |
B.1.1.7 |
715(84.6%with,contacts) |
98937(69.7%with,contacts) |
0.7% |
1.9%(1.7%-2.2%) [233/12055] |
11.0%(10.9%-11.2%)[19671/178585] |
| VOC-20DEC02 |
B.1.351 |
102(64.7%with,contacts) |
102(64.7%with,contacts) |
50.0% |
3.7%(2.6%-5.2%)[29/787] |
9.1%(5.7%-14.3%)[16/176] |
| VOC-21JAN-02 |
P.1 |
5(100.0%with,contacts) |
5(80.0%with,contacts) |
50.0% |
Unavailable[0/86] |
Unavailable[1/8] |
| VOC-21FEB-02 |
B.1.1.7withE484K |
1(100.0%with,contacts) |
33(81.8%with,contacts) |
2.9% |
Unavailable[0/96] |
0.0%(0.0%-3.3%)[0/111] |
| VUI-21JAN-01 |
P.2 |
3(66.7%with,contacts) |
30(76.7%with,contacts) |
9.1% |
Unavailable[0/137] |
11.1%(5.5%-21.2%)[7/63] |
| VUI-21FEB-01 |
A.23.1withE484K |
0(0with,contacts) |
62(61.3%with,contacts) |
0.0% |
Unavailable[0/0] |
8.6%(4.4%-16.1%)[8/93] |
| VUI-21FEB-03 |
B.1.525 |
85(69.4%with,contacts) |
105(71.4%with,contacts) |
44.7% |
1.0%(0.6%-1.6%)[19/1882] |
9.3%(5.9%-14.4%)[17/182] |
| VUI-21FEB-04 |
B.1.1.318 |
16(87.5%with,contacts) |
31(74.2%with,contacts) |
34.0% |
Unavailable[3/280] |
3.6%(1.0%-12.1%)[2/56] |
| VUI-21MAR-01 |
B.1.324.1 with E484K |
1(100.0%with contacts) |
0(0 with contacts) |
100.0% |
Unavailable[0/7] |
Unavailable[0/0] |
| VUI-21MAR-02 |
P.3 |
3 (33.3% with contacts) |
1 (100.0% with contacts) |
75.0% |
Unavailable[0/4] |
Unavailable[0/3] |
Secondary attack rates marked as ‘Unavailable’ when count of contacts is less than 50 or count of exposing cases is less than 20.
Travel-linked cases for secondary attack rates are identified positively in NHS Test and Trace data using multiple PHE sources. A
case is considered as being travel-linked if:
1. EpiCell or Health Protection Teams has found evidence of international travel
2. their NHS Test and Trace record mentions an event associated with international travel
3. their NHS Test and Trace record was created after notification via IHR NFP
4. they have been marked for priority contact tracing in NHS Test and Trace for reasons of travel
Some travel-linked cases may be missed by these methods and would be marked as non-travel-linked or unknown. Secondary
attack rates from NHS Test and Trace should generally be considered lower bounds due to the nature of contact tracing and
testing. Data provided is for period 5 January 2021 to 7 March 2021 in order to allow time for contacts to become cases, hence
case counts are lower than other sources.
Spatial variation in risk for variants
Spatial variation in risk
The spatial risk surface is estimated by comparing the smoothed intensity of cases (variants
of concern) and controls (PCR +ve, non-variants of concern) across a defined geographical
area to produce an intensity (or risk) ratio. If the ratio is ~1, this suggests that the risk of
infection is unrelated to spatial location. Evidence of spatial variation in risk occurs where the
intensities differ. Ratio values >1 indicate an increased risk and values <1 indicate lower risk.
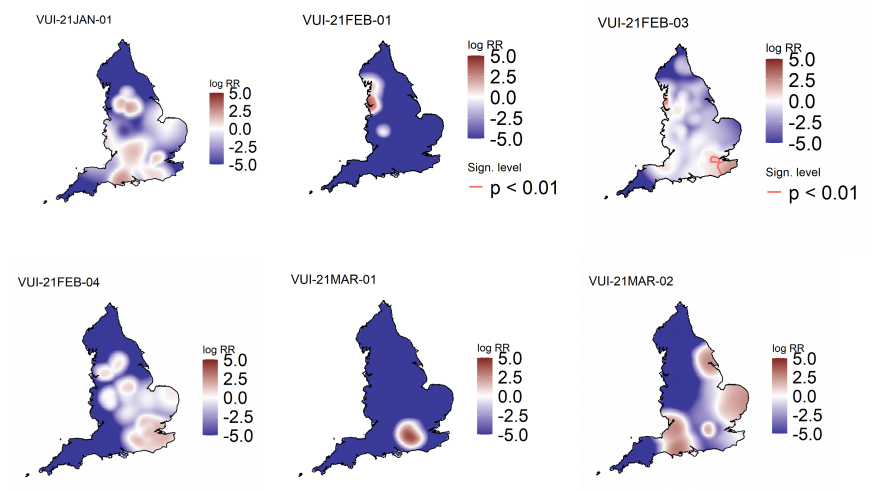
Figure 5 highlights areas of significantly increased risks for variants of concern, areas of
significantly increased risk were identified for all variants of concern other than VOC-21JAN02
(P.1). Supplementary data is not available for this figure. Figure 6 highlights areas of
significantly increased risks for variants under investigation, areas of significantly increased
risk were identified for VUI-21FEB-01 (A23.1 +E484K) and VUI-21FEB-03 (B.1.525) only.
Supplementary data is not available for this figure.
Figure 5. Spatial variation in risk for VOC data from 1 October 2020, as of 31 March 2021 (Supplementary data is not available for this figure)
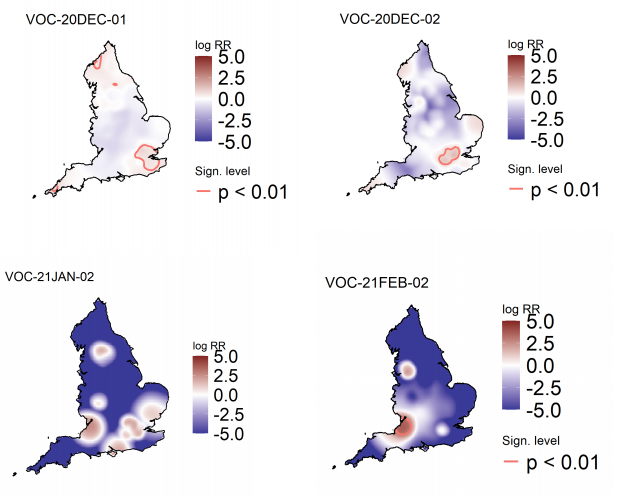 Figure 6. Spatial variation in risk for VUI data from 1 October 2020, as of 31 March 2021 (Supplementary data is not available for this figure)
Figure 6. Spatial variation in risk for VUI data from 1 October 2020, as of 31 March 2021 (Supplementary data is not available for this figure)
Appendices
Appendix 1. Variant assessment tools
Repository of human and machine readable genomic case definitions
A repository containing the up-to-date genomic definitions for all VOC and VUI as curated by
Public Health England was created 5 March 2021. The repository can be accessed on
GitHub. They are provided in order to facilitate standardised VOC and VUI calling across
sequencing sites and bioinformatics pipelines and are the same definitions used internally at
Public Health England. Definition files are provided in YAML format so are compatible with a
range of computational platforms. The repository will be regularly updated. The genomic and
biological profiles of VOC and VUI are also detailed on first description in prior technical
briefings.
Variant risk assessment framework
Variant risk assessment includes the following confidence grading categorisations and
utilises the framework in Table 5.
1. Low: Little or poor-quality evidence, uncertainty or conflicting views amongst
experts, no experience with previous similar incidents.
2. Moderate: Adequate quality evidence, including consistent results published only
in grey literature, reliable source(s), assumptions made on analogy and agreement
between experts or opinion of at least 2 trusted experts.
3. High: Good quality evidence, multiple reliable sources, verified, expert opinion
concurs, experience of previous similar incidents.
Table 5. Variant risk assessment framework
| Indicator |
Risk assessment framework |
| Zoonotic emergence and transmission to humans |
Animal reservoir identified but no
evidence of transmission from animals to humans |
Sporadic transmission from
animals to humans |
Frequent transmission from animals to humans |
|
| Transmissibility between humans |
No demonstrated person to person transmission |
Limited human case clusters |
Established human to human transmission, which appears similar to wild type virus |
Transmissibility appears greater than the wild type virus |
| Infection severity |
Evidence of less severe clinical picture or lower infection fatality than from wild type SARS-CoV2 infections |
Similar clinical picture and
infection fatality to wild type SARS-CoV-2 infections OR experimental animal data
suggesting potential for increased disease severity humans |
More severe clinical picture or higher infection fatality than from wild type SARS-CoV-2 infections (limited to specific
risk groups) |
More severe clinical picture or higher infection fatality than from wild type SARS-CoV-2 infections |
| Susceptibility and immunity – natural infection |
Evidence of no antigenic difference from other circulating wild type virus |
Structural data suggesting
antigenic difference from other circulating wild type virus |
Experimental evidence of
functional evasion of naturally acquired immunity |
Evidence of frequent infection
in humans with known prior infection with earlier virus variant. |
| Vaccines |
Evidence of no structural or antigenic difference in vaccine targets |
Structural data suggesting difference in vaccine target epitopes |
Experimental evidence of functional evasion of vaccine derived immunity |
Evidence of frequent vaccine
failure or decreased effectiveness in humans |
| Drugs and therapeutics |
Evidence of no structural or antigenic difference in
therapeutic targets |
Structural data suggesting difference in therapeutic target
epitopes |
Experimental evidence of reduced drug susceptibility |
Evidence of frequent drug or therapeutic failure or decreased effectiveness in humans |
Appendix 2. Data on individual variants
VOC-20DEC-01 (B.1.1.7)
This variant was designated VUI 202012/01 (B.1.1.7) on detection and on review redesignated
as VOC-20DEC-01 (202012/01, B.1.1.7) on 18 December 2020.
Genomic profile
Lineage defining mutations are shown in technical briefing 6. In addition, VOC-20DEC-01 has
acquired other mutations in some cases (Table 6).
Table 6. VOC-20DEC-01 (B.1.1.7) Spike mutations acquired in addition to the variant defining mutations 11 December 2020 to 10 March 2021.
Percentages are the proportion of all sequences of of VOC-20DEC-01 (B.1.1.7) per time
period with the mutation.
| VOC-20DEC-01 (B.1.1.7) Spike variants |
| Amino acid change |
Total number of instances in VOC-20DEC01 (B.1.1.7)(UK data) to 31 March 2021 |
31 December 2020 to 30 January 2021 |
31 January 2021 to
27 February 2021 |
28 February 2021 to 31 March 2021 |
| L18F |
4943(2.57%) |
1417(1.97%) |
938(1.65%) |
576(1.46%) |
| Q677H |
1510(0.78%) |
342(0.48%) |
572(1.01%) |
480(1.21%) |
| G142V |
305(0.16%) |
22(0.03%) |
118(0.21%) |
132(0.33%) |
| F490S |
227(0.12%) |
47(0.07%) |
63(0.11%) |
92(0.23%) |
| A475A |
233(0.12%) |
54(0.08%) |
51(0.09%) |
88(0.22%) |
| S680F |
182(0.09%) |
25(0.03%) |
72(0.13%) |
54(0.14%) |
| S494P |
852(0.44%) |
357(0.5%) |
182(0.32%) |
47(0.12%) |
| Y144F |
435(0.23%) |
148(0.21%) |
126(0.22%) |
32(0.08%) |
| L455F |
76(0.04%) |
18(0.03%) |
17(0.03%) |
28(0.07%) |
| A684V |
81(0.04%) |
22(0.03%) |
19(0.03%) |
25(0.06%) |
| K458N |
29(0.02%) |
1(0%) |
0(0%) |
22(0.06%) |
| Q677H(alt) |
52(0.03%) |
19(0.03%) |
16(0.03%) |
16(0.04%) |
| H146Y |
99(0.05%) |
20(0.03%) |
40(0.07%) |
15(0.04%) |
| E484K |
96(0.05%) |
37(0.05%) |
34(0.06%) |
14(0.04%) |
| F490Y |
18(0.01%) |
0(0%) |
5(0.01%) |
13(0.03%) |
| N148S |
28(0.01%) |
7(0.01%) |
8(0.01%) |
12(0.03%) |
| K150R |
25(0.01%) |
1(0%) |
11(0.02%) |
12(0.03%) |
| T678I |
189(0.1%) |
44(0.06%) |
71(0.13%) |
11(0.03%) |
| S12P |
26(0.01%) |
6(0.01%) |
7(0.01%) |
11(0.03%) |
| Q493R |
26(0.01%) |
3(0%) |
8(0.01%) |
11(0.03%) |
| G504S |
16(0.01%) |
1(0%) |
5(0.01%) |
10(0.03%) |
| Total VOC-20DEC-01 (B.1.1.7) 192,689 |
International Epidemiology
Lineage B.1.1.7 is dispersed across the UK. Confirmed cases are those identified by whole
genome sequencing. As of 31 March 2021, there were 151,344 confirmed and probable
cases of VOC 202012/01 (B.1.1.7) in England. The use of S gene target failure (SGTF) in the
Taqpath assay as a good proxy for cases of this variant of concern has been described in
prior technical briefings. In samples tested with this assay in the Lighthouse Laboratories,
samples with SGTF have predominated since mid December 2020, reaching 99% of cases in
the week starting 3 March 2021. Proportions in all regions were >97% in March 2021 (prior
technical briefings). An online B.1.1.7 tracking tool is available https://covid19.sanger.ac.uk.
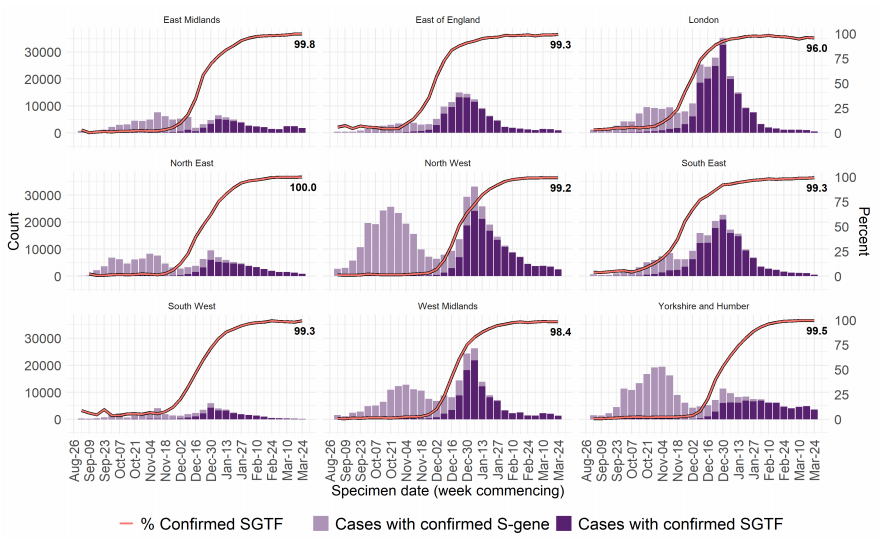
Figure 7 and Figure 8 show the weekly number and proportion of England Pillar 2
(community testing) COVID-19 cases with SGTF among those tested with the TaqPath
assay, and with S gene detection results, showing cases with SGTF account for more than
99% of cases from community testing nationally and over 96% in all regions. The
supplementary data for figures is available here.
International Epidemiology
As of the 31 March 2021, there are 130 countries or territories (including the UK) reporting
cases of VOC-20DEC-01 globally. Of countries or territories outside of the UK, 31 report, or
there is evidence of, community transmission. However, for many countries the information
available on the extent of transmission within the country is not clear.
Figure 7. Weekly number and proportion of England Pillar 2 COVID-19 cases with SGTF among those tested with the
TaqPath assay and with S gene detection results (1 September 2020 to 9 March 2021) (Find accessible data used in this graph in Variants of concern: technical briefing 8 – underlying data.)
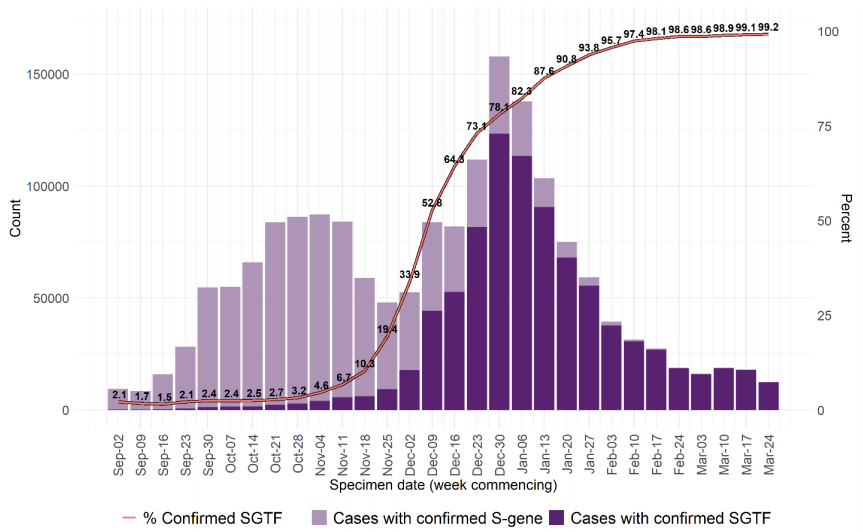 Figure 8. Weekly number and proportion of England Pillar 2 COVID-19 cases with SGTF among those tested with the
TaqPath assay and with S gene detection results, by region of residence (1 September 2020 to 9 March 2021) (Find accessible data used in this graph in Variants of concern: technical briefing 8 – underlying data.)
Figure 8. Weekly number and proportion of England Pillar 2 COVID-19 cases with SGTF among those tested with the
TaqPath assay and with S gene detection results, by region of residence (1 September 2020 to 9 March 2021) (Find accessible data used in this graph in Variants of concern: technical briefing 8 – underlying data.)
VOC-21FEB-02 (B.1.1.7 cluster with E484K)
Through routine scanning of variation in VOC-20DEC-01 (B.1.1.7) a small number of B.1.1.7
sequences had acquired the spike protein mutation E484K. Information suggested more than
one independent acquisition event. One cluster was predominant with evidence of community
transmission and was designated variant under investigation on detection and on review redesignated as variant of concern VOC-21FEB-02 (VOC202102/02, B.1.1.7 cluster with
E484K) on 5 February 2021. The genomic and biological profile is as previously described
Epidemiological profile
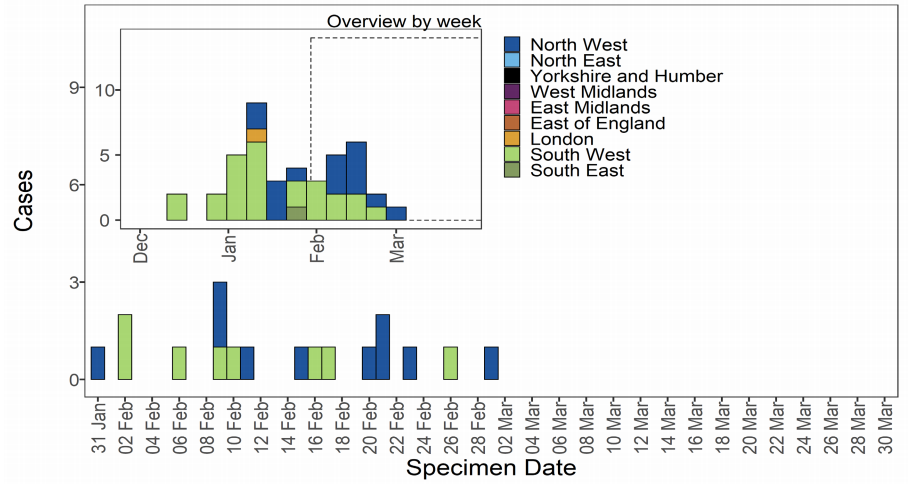
As of 31 March 2021, 43 genomically confirmed cases of VOC-21FEB-02 (B.1.1.7) have
been identified; concentrated in the South West and North West (Table 7). Cases by
specimen date are shown in Figure 9 and shows cases have not been detected since 1
March 2021. The supplementary data for figures is available here. This variant will not be
included in future technical briefings unless a new case is detected.
International Epidemiology
As of the 31 March 2021, international cases have been reported in 3 countries and 5
sequences from the Netherlands have been identified on GISAID.
Table 7. Number of confirmed and probable VOC-21FEB-02 (B.1.1.7 cluster with E484K) cases, by region of residence as of 31 March 2021
| Region |
Case Number |
Case Proportion |
| London |
1 |
2.3% |
| North West |
15 |
34.9% |
| South East |
1 |
2.3% |
| South West |
26 |
60.5% |
Figure 9. Confirmed and probable VOC-21FEB-02 (B.1.1.7 cluster with E484K) cases by specimen date as of 31 March
2021. Larger plot includes last 60 days only. (Find accessible data used in this graph in Variants of concern: technical briefing 8 – underlying data.)
VOC-20DEC-02 (B.1.351)
B.1.351 was initially detected in South Africa. This variant was designated variant under investigation on detection and on review redesignated
as VOC-20DEC-02 (B.1.351) on 24 December 2020. The clinical risk assessment for VOC-20DEC-02 is shown in Table 8.
Table 8. Risk assessment for VOC-20DEC-02 (B.1.351)
| Indicator |
RAG* |
Confidence |
Assessment and rationale |
| Zoonotic emergence |
|
NA |
Not applicable |
| Transmissibility between humans |
|
LOW |
Transmissibility does not appear to exceed wild type virus in UK (B.1.1.7) context
(MODERATE confidence). Epidemiology which could be related to increased
transmissibility has been observed in other countries (LOW confidence). If a selective
advantage were to be conferred by increased population immunity, this may alter the
current position in the UK. |
| Infection severity |
|
|
Insufficient information |
| Naturally acquired immunity |
|
MODERATE |
There is laboratory evidence of reduction in susceptibility to naturally acquired immunity
from strains from the early pandemic (MODERATE CONFIDENCE) and epidemiological
evidence of high levels of population immunity in SA when this variant emerged and spread
rapidly, raising the possibility of reinfections. Systematic comparative data on clinical
reinfections is required to raise the risk to red. |
| Vaccine derived immunity |
|
MODERATE |
There is laboratory evidence of reduced neutralisation by sera from vaccinated individuals,
across multiple studies and vaccines. New evidence suggests the magnitude of this effect
is larger for B.1.351, compared to P.1 or B.1.1.7 (MODERATE CONFIDENCE). There is
clinical trial evidence of decreased effectiveness in humans for preventing mild to moderate
infection (MODERATE CONFIDENCE); this varies by vaccine. However, the trials were not able to measure the impact on severe disease including hospitalisation and mortality
(INSUFFICIENT INFORMATION for prevention of hospitalisation and death). |
| Drugs and Therapeutics |
|
MODERATE |
There is experimental evidence that variants containing E484K may have reduced susceptibility to some monoclonal antibody based therapies in laboratory conditions (MODERATE confidence). |
| Overall assessment of level and nature of risk, and level of confidence |
|
|
B.1.351 is a successful lineage in South Africa and is becoming successful internationally, including in Europe. It remains at a low prevalence in England. Monitoring is required as lockdown eases and the vaccinated population increases.
There is increasingly robust laboratory data supporting antigenic distance between B.1.351
and older viruses, and there is clinical trial evidence of a reduction in vaccine efficacy
relating to infection, but insufficient evidence to assess any impact on prevention of severe
disease or death. |
Epidemiological profile
VOC-20DEC-02 (B1.351) is dispersed across the UK in low numbers. Confirmed cases are
those identified by whole genome sequencing; probable cases are COVID-19 cases without
sequencing, but who are contacts of confirmed cases. As of 31 March 2021, 410 confirmed
and probable cases of VOC-20DEC-02 (B.1.351) were identified. An international travel link
was identified for 258 cases, and 103 had no travel link. Confirmed and probable cases by
specimen date are shown in Figure 10, and regional breakdown in Table 9. Figure 10 shows
cases predominate in the London area. The supplementary data for figures is available here.
Figure 10. Confirmed and probable VOC-20DEC-02 (B.1.351) cases by specimen date as of 31 March 2021. (Find accessible data used in this graph in Variants of concern: technical briefing 8 – underlying data.)
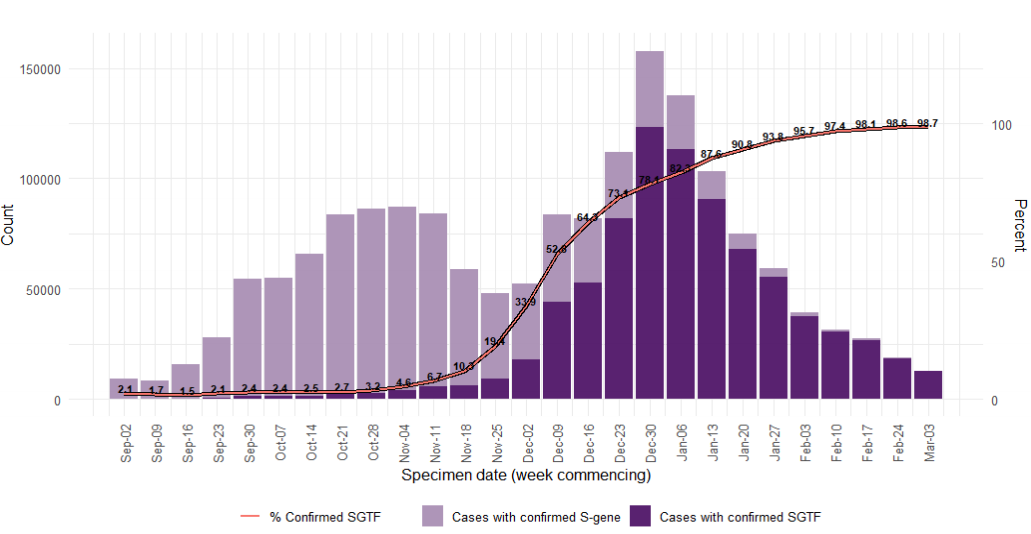
Table 9. Confirmed and probable cases of VOC-20DEC-02 by region as of 31 March 2021
| Region |
Case Number |
Case Proportion |
| East Midlands |
16 |
3.9% |
| East of England |
45 |
11.0% |
| London |
170 |
41.5% |
| North East |
7 |
1.7% |
| North West |
53 |
12.9% |
| South East |
62 |
15.1% |
| South West |
14 |
3.4% |
| West Midlands |
31 |
7.6% |
| Yorkshire and Humber |
12 |
2.9% |
International Epidemiology
As of 31 March 2021 there are 89 countries (including the UK) that have reported cases of
this variant globally. GISAID (gisaid.org) includes data on sequences available
internationally. As of the 31 March 2021 5,282 sequences of VOC-20DEC-02, excluding
UK, are available from 59 countries/territories.
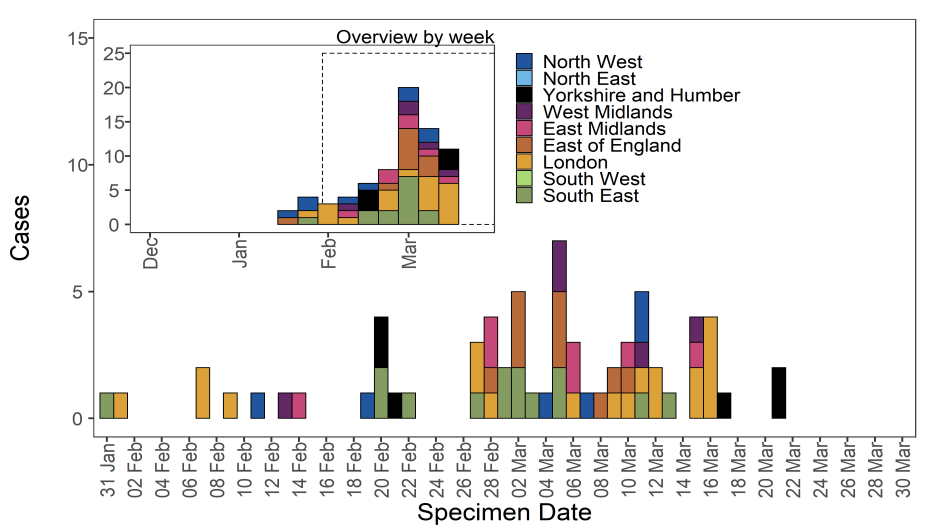
VOC-21JAN-02 (P.1)
First identified in Japan amongst travellers from Brazil, the P.1 lineage is a descendant of
B.1.1.28. This variant was designated variant under investigation on detection and on
review re-designated as VOC-21JAN-02 (P.1) on 13 January 2021. The clinical risk
assessment for P1 is detailed in technical briefing 7.
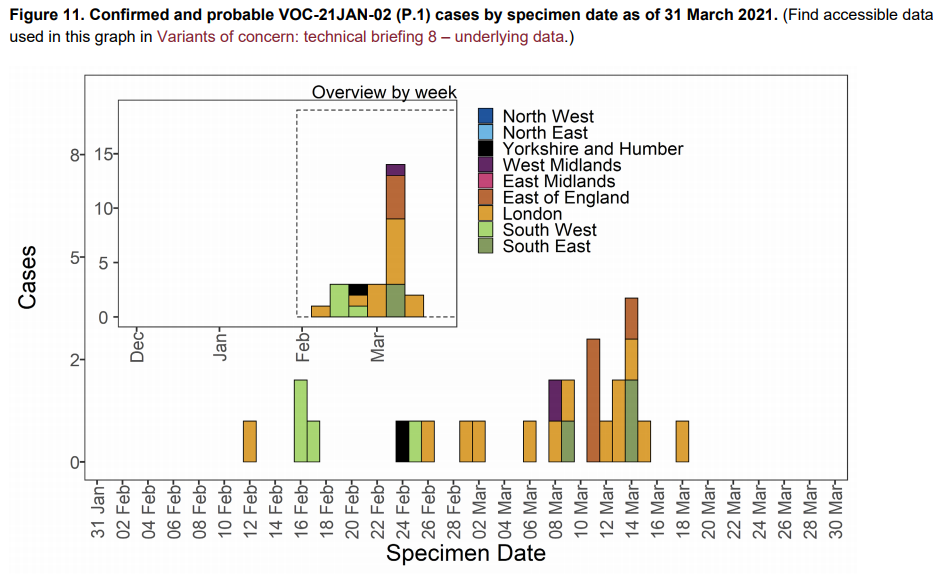
Epidemiological profile
As of 31 March 2021, 27 genomically confirmed and probable cases of VOC-21JAN-02
(P.1) have been identified in England. 23 cases have been linked to international travel.
Regional breakdown of cases in shown in Table 10 and cases by specimen date are shown
in Figure 11. The supplementary data for figures is available here.
Table 10. Number of confirmed and probable cases VOC-21JAN-02 (P.1), by region of residence as of 31 March 2021.
| Region |
Case Number |
Case Proportion |
| East of England |
4 |
14.8% |
| London |
13 |
48.1% |
| South East |
3 |
11.1% |
| South West |
5 |
18.5% |
| West Midlands |
1 |
3.7% |
| Yorkshire and Humber |
1 |
3.7% |
Figure 11. Confirmed and probable VOC-21JAN-02 (P.1) cases by specimen date as of 31 March 2021. (Find accessible data used in this graph in Variants of concern: technical briefing 8 – underlying data.)
 International Epidemiology
International Epidemiology
As of 31 March 2021, cases of VOC-21JAN-02 (P.1) have been reported in 38 countries or
territories. Ten countries have reported cases of a Brazilian variant additional information
is awaited to clarify if this is with VOC-21JAN-02 (P.1).
GISAID includes data on sequences available internationally. As of the 31 March 2021
1,360 sequences of VOC-21JAN-02 are listed from 30 countries excluding the UK
VUI-21JAN-01 (P2)
First identified in Brazil, the P.2 lineage is a descendant of B.1.1.28. This variant was
designated VUI-21JAN-01 (P.2) on 13 January 2021. It was first sequenced in the UK in
November 2020.
Epidemiological profile
As of 31 March 2021, 53 cases of VUI-21JAN-01 (P.2) have been identified in England. 9
cases have been linked to international travel, and 40 cases had no travel link. Regional
breakdown of cases in shown in Table 11 and confirmed and probable cases by specimen
date are shown in Figure 12. Figure 12 shows a limited number of cases in different
regions. The supplementary data for figures is available here
Table 11. Number of confirmed and probable cases VUI-21JAN-01 (P.2), by region of residence as of 31 March 2021
| Region |
Case Number |
Case Proportion |
| East Midlands |
1 |
1.9% |
| East of England |
2 |
3.8% |
| London |
14 |
26.4% |
| North West |
11 |
20.8% |
| South East |
6 |
11.3% |
| South West |
1 |
13.2% |
| West Midlands |
1 |
1.9% |
| Yorkshire and Humber |
11 |
20.8% |
International Epidemiology
As of 31 March 2021, cases of VUI-21JAN-01 (P.2) have been reported in 32 countries or
territories. GISAID (gisaid.org) includes data on sequences available internationally. As of
31 March 2021 1,558 sequences (excluding UK) of VUI-21JAN-01 from 29 countries.
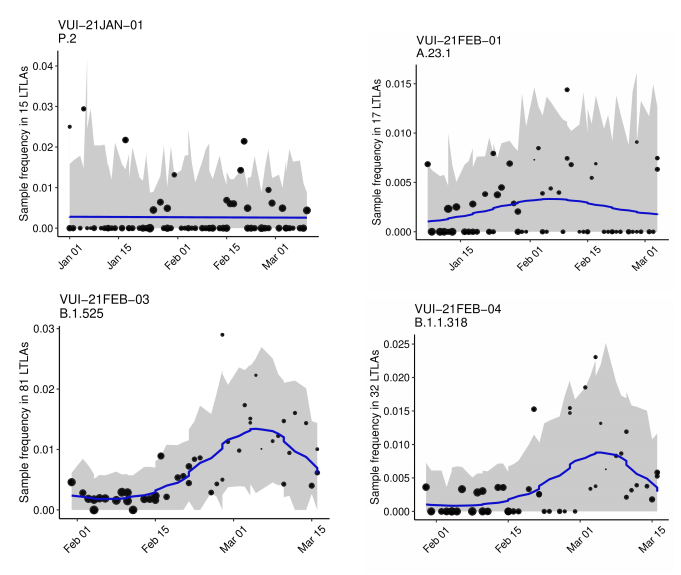
Figure 12. Confirmed and probable VUI-21JAN-01 (P.2) cases by specimen date, as of 31 March 2021. (Find accessible data used in this graph in Variants of concern: technical briefing 8 – underlying data.)
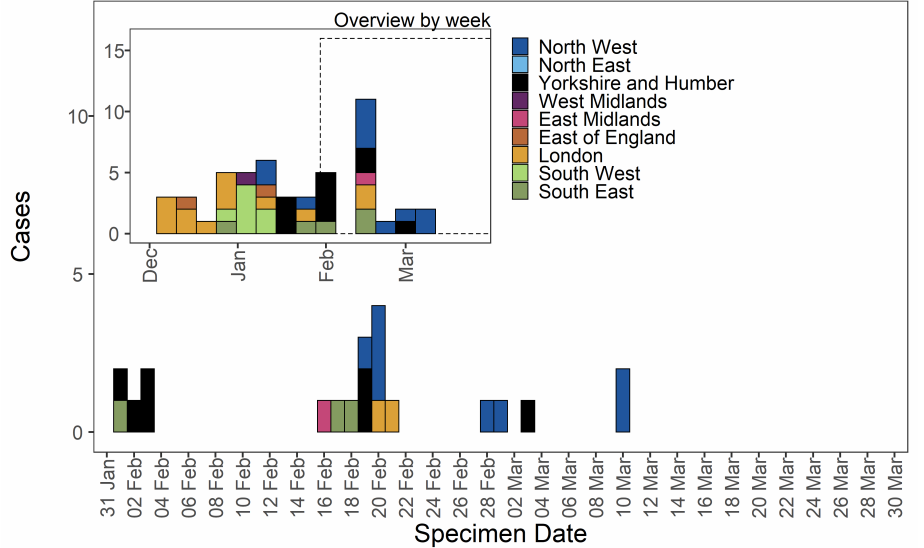 VUI-21FEB-01 (A.23.1 with E484K)
VUI-21FEB-01 (A.23.1 with E484K)
This variant was first identified in Liverpool, UK, derived from a lineage first identified in
Uganda without E484K. The variant was designated VUI-21FEB-01 (A.23.1 with E484K)
on 5 February 2021. It was first detected in the UK in December 2020.
Epidemiological profile
As of 31 March 2021, 78 genomically confirmed cases of VUI-21FEB-01 (A.23.1 with
E484K) have been identified. The majority of these are residents of the North West of
England (Table 12). Confirmed and probable cases by specimen date are shown in Figure
13. Figure 13 shows cases predominate in the North West with no cases detected as of
the 23 February 2021. The supplementary data for figures is available here.
International Epidemiology
The are no cases reported internationally as of the 31 March 2021. GISAID includes data
on sequences available internationally. As of 31 March 2021 1 sequence is listed of VUI21FEB-01
(A.23.1 with E484K) (excluding UK) from Netherlands.
Table 12. Number of confirmed and probable VUI-21FEB-01 (A.23.1 with E484K) cases, by region of residence as of 31 March 2021
| Region |
Case Number |
Case Proportion |
| North West |
77 |
98.7% |
| West Midlands |
1 |
1.3% |
Figure 13. Confirmed and probable VUI-21FEB-01 (A.23.1 with E484K) cases by specimen date as of 31 March 2021. Larger
plot includes last 60 days only. (Find accessible data used in this graph in Variants of concern: technical briefing 8 – underlying data.)
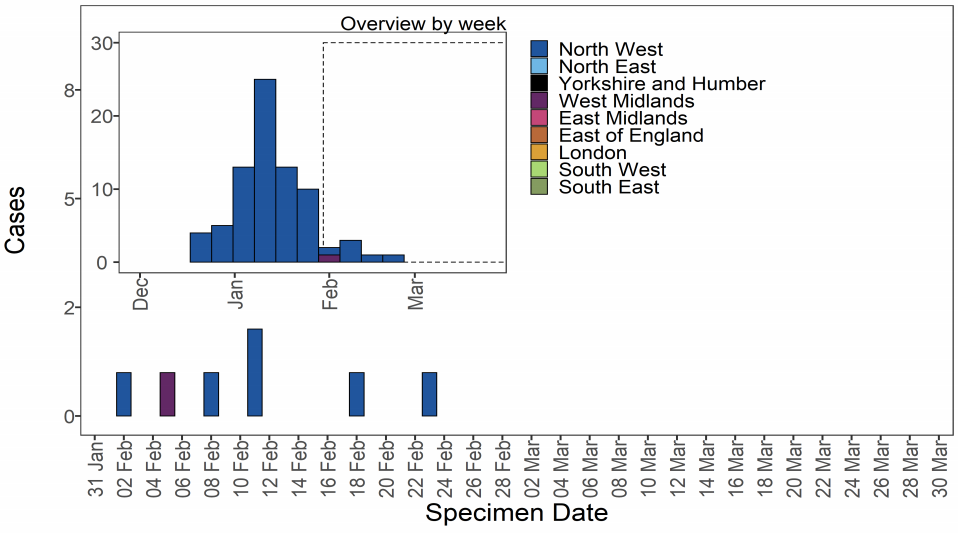
VUI-21FEB-03 (B.1.525)
First identified as a geographically dispersed cluster in UK on the 2 February 2021. This
variant was designated VUI-21FEB-03 (B.1.525) on 12 February 2021. The earliest
sample date for VUI-21FEB-03 (B.1.525) in England was 15 December 2020. The
biological profile is described in technical briefing 7.
Epidemiological profile
As of 31 March 2021, there were 277 cases of VUI-21FEB-03 (B.1.525) in England In this
geographically dispersed genomic cluster with likely community transmission. Regional
cases are shown in Table 13 and confirmed and probable cases by specimen date are
shown in Figure 14. Figure 14 shows cases are in several regions, predominating in
London and South East and North West. The supplementary data for figures is available
here.
Table 13. Number of confirmed and probable cases VUI-21FEB-03 (B.1.525 by region of residence as of 31 March 2021
| Region |
Case Number |
Case Proportion |
| East Midlands |
8 |
2.9% |
| East of England |
17 |
6.1% |
| London |
86 |
31.0% |
| North East |
2 |
0.7% |
| North West |
60 |
21.7% |
| South East |
62 |
22.4% |
| South West |
11 |
4.0% |
| West Midlands |
17 |
6.1% |
| Yorkshire and Humber |
14 |
5.1% |
Figure 14. Confirmed and probable cases VUI-21FEB-03 (B.1.525) by specimen date as of 31 March 2021. Larger plot includes last 60 days only. (Find accessible data used in this graph in Variants of concern: technical briefing 8 – underlying data.)
 International Epidemiology
International Epidemiology
As of 31 March 2021, cases of VUI-21FEB-03 (B.1.525) have been reported in 39
countries or territories.
GISAID includes data on sequences available internationally. As of the 31 March 2021 652
sequences of VUI-21FEB-03 (B.1.525) are listed, from 34 countries or territories excluding
UK
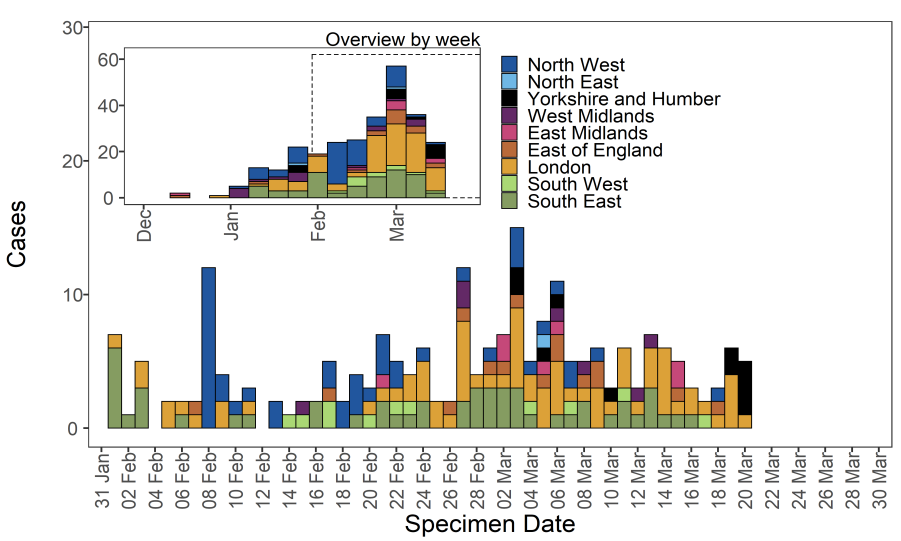
VUI-21FEB-04 (B.1.1.318)
The VUI-21FEB-04 is lineage B.1.1.318 and was identified in England in mid February
2021 through routine horizon scanning for the development of new clusters of genomes
containing E484K. This analysis identified an initial cluster of 6 cases containing E484K
and other spike mutations, designated VUI-21FEB-04 (B.1.1.318) on 23 February 2021
Epidemiological profile
As of 31 March 2021, there were 72 genomically confirmed cases of VUI-21FEB-04
(B.1.1.318). Cases have occurred in most regions of England, concentrated in London and
the South Eastble 10). Regional cases are shown in Table 14 and confirmed and probable
cases by specimen date are shown in Figure 15. Figure 15 shows sporadic cases in
several regions. The supplementary data for figures is available here. Of the 72 cases, 34
were travel associated countries and 2 were contacts of travellers. 13 cases had no known
link to travel.
International Epidemiology
As of 31 March 2021 there are no cases reported internationally.
GISAID (gisaid.org) includes data on sequences available internationally. As of the 31
March 2021, there are 2 international VUI-21FEB-04 sequences, excluding UK. (Germany
1, USA 1).
Table 14. Number of confirmed and probable VUI-21FEB-04 (B.1.1.318) cases, by region of residence as of 31 March 2021
| Region |
Case Number |
Case Proportion |
| East Midlands |
7 |
9.7% |
| East of England |
11 |
15.3% |
| London |
20 |
27.8% |
| North West |
9 |
12.5% |
| South East |
14 |
19.4% |
| West Midlands |
5 |
6.9% |
| Yorkshire and Humber |
6 |
8.3% |
Figure 15. Confirmed and probable VUI-21FEB-04 (B.1.1.318) cases by specimen date as of 31 March 2021. Larger plot
includes last 60 days only. (Find accessible data used in this graph in Variants of concern: technical briefing 8 – underlying data.)
VUI-21MAR-01 (B.1.324.1 with E484K)
First identified via horizon scanning of genomes with spike mutations characteristic of
VOCs (including both N501Y and E484K) on 3 March 2021, the variant VUI-21MAR-01
(B.1.324.1 with E484K) was designated VUI on detection as VUI-21MAR-01 (B.1.324.1
with E484K) on 4 March 2021.
Epidemiological profile
As of 31 March 2021, there are 2 confirmed cases in the UK in a group of returning
travellers, with links to additional unsequenced cases.
Epidemiological profile
As of 31 March 2021 there are no cases reported internationally.
GISAID (gisaid.org) includes data on sequences available internationally. As of the 31
March 2021, 0 sequences are listed internationally of VUI-21MAR-01.
VUI-21MAR-02 (P.3)
The VUI-21MAR-02 (P.3) was identified on 9 March 2021 in a report of 33 genomes from
the Philippines with 13 lineage defining mutations. This variant shares important mutations
with Variants of Concern including E484K, N501Y and P681H. Based on genomic profile,
PHE has designated VUI-21MAR-02 (P.3) on the 11 March 2021. This variant arises from
B.1.1.28, the same parent lineage that gave rise to P.1 and P.2 in Brazil. Phylogenetic
analysis of P.3 shows diversity indicating circulation prior to detection.
Epidemiological profile
As of 31 March 2021, there are 5 confirmed cases in the UK cases, of which 4 have recent
travel history.
International Epidemiology
As of 31 March 2021, cases of VUI-21MAR-02 (P.3) have been reported in 6 countries or
territories.
GISAID includes data on sequences available internationally. As of the 31 March 2021, 91
sequences are listed internationally of VUI-21MAR-02 excluding UK. (Australia 2,
Germany 3, Japan 1, New Zealand 2, Norway 2, Philippines 81).
Appendices
Epidemiological profile
As of 10 March 2021, there are 2 confirmed cases in the UK in a single group of returning
travellers. Two additional households note contact of which one has tested positive, sequence
data not available. There is no current evidence of spread in the UK based on sequencing data.
No deaths were reported.
International Epidemiology
As of 8 March 2021 there are no cases reported internationally.
GISAID (gisaid.org) includes data on sequences available internationally. As of the 10 March
2021, 0 sequences are listed internationally of VUI 202103/01 (B.1.324.1 with E484K).
Sources and acknowledgments
Data sources
Data used in this investigation is derived from the COG-UK dataset, the PHE Second
Generation Surveillance System (SGSS), NHS Test and Trace, the Secondary Uses
Service (SUS) dataset and Emergency Care Data Set (ECDS).
Variant Technical Group
Authors of this report
PHE Genomics Cell
PHE Outbreak Surveillance Team
PHE Epidemiology Cell
PHE Contact Tracing Data Cell
Variant Technical Group Membership
The PHE Variant Technical Group includes representation from the following
organisations: PHE, DHSC, BEIS, Public Health Wales , Public Health Scotland, Public
Health Agency Northern Ireland, Imperial College London, London School of Hygiene and
Tropical Medicine, University of Birmingham, University of Cambridge, University of
Edinburgh, University of Liverpool, the Wellcome Sanger Institute.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to those teams and groups providing data for this analysis
including: the Lighthouse Laboratories, COG-UK, the Wellcome Sanger Institute, tthe PHE
Epidemiology Cell, Contact Tracing, Genomics and Outbreak Surveillance Teams.
Published: April 2021
PHE gateway number: GW-7909
 Figure 2. Variant prevalence for all England available case data from 1 February 2021 to 21 March 2021 excluding VOC20DEC-01.(Find accessible data used in this graph in Variants of concern: technical briefing 8 – underlying data.)
Figure 2. Variant prevalence for all England available case data from 1 February 2021 to 21 March 2021 excluding VOC20DEC-01.(Find accessible data used in this graph in Variants of concern: technical briefing 8 – underlying data.)




 Figure 6. Spatial variation in risk for VUI data from 1 October 2020, as of 31 March 2021 (Supplementary data is not available for this figure)
Figure 6. Spatial variation in risk for VUI data from 1 October 2020, as of 31 March 2021 (Supplementary data is not available for this figure)

 Figure 8. Weekly number and proportion of England Pillar 2 COVID-19 cases with SGTF among those tested with the
TaqPath assay and with S gene detection results, by region of residence (1 September 2020 to 9 March 2021) (Find accessible data used in this graph in Variants of concern: technical briefing 8 – underlying data.)
Figure 8. Weekly number and proportion of England Pillar 2 COVID-19 cases with SGTF among those tested with the
TaqPath assay and with S gene detection results, by region of residence (1 September 2020 to 9 March 2021) (Find accessible data used in this graph in Variants of concern: technical briefing 8 – underlying data.)



 International Epidemiology
As of 31 March 2021, cases of VOC-21JAN-02 (P.1) have been reported in 38 countries or
territories. Ten countries have reported cases of a Brazilian variant additional information
is awaited to clarify if this is with VOC-21JAN-02 (P.1).
GISAID includes data on sequences available internationally. As of the 31 March 2021
1,360 sequences of VOC-21JAN-02 are listed from 30 countries excluding the UK
VUI-21JAN-01 (P2)
First identified in Brazil, the P.2 lineage is a descendant of B.1.1.28. This variant was
designated VUI-21JAN-01 (P.2) on 13 January 2021. It was first sequenced in the UK in
November 2020.
Epidemiological profile
As of 31 March 2021, 53 cases of VUI-21JAN-01 (P.2) have been identified in England. 9
cases have been linked to international travel, and 40 cases had no travel link. Regional
breakdown of cases in shown in Table 11 and confirmed and probable cases by specimen
date are shown in Figure 12. Figure 12 shows a limited number of cases in different
regions. The supplementary data for figures is available here
International Epidemiology
As of 31 March 2021, cases of VOC-21JAN-02 (P.1) have been reported in 38 countries or
territories. Ten countries have reported cases of a Brazilian variant additional information
is awaited to clarify if this is with VOC-21JAN-02 (P.1).
GISAID includes data on sequences available internationally. As of the 31 March 2021
1,360 sequences of VOC-21JAN-02 are listed from 30 countries excluding the UK
VUI-21JAN-01 (P2)
First identified in Brazil, the P.2 lineage is a descendant of B.1.1.28. This variant was
designated VUI-21JAN-01 (P.2) on 13 January 2021. It was first sequenced in the UK in
November 2020.
Epidemiological profile
As of 31 March 2021, 53 cases of VUI-21JAN-01 (P.2) have been identified in England. 9
cases have been linked to international travel, and 40 cases had no travel link. Regional
breakdown of cases in shown in Table 11 and confirmed and probable cases by specimen
date are shown in Figure 12. Figure 12 shows a limited number of cases in different
regions. The supplementary data for figures is available here
 VUI-21FEB-01 (A.23.1 with E484K)
This variant was first identified in Liverpool, UK, derived from a lineage first identified in
Uganda without E484K. The variant was designated VUI-21FEB-01 (A.23.1 with E484K)
on 5 February 2021. It was first detected in the UK in December 2020.
Epidemiological profile
As of 31 March 2021, 78 genomically confirmed cases of VUI-21FEB-01 (A.23.1 with
E484K) have been identified. The majority of these are residents of the North West of
England (Table 12). Confirmed and probable cases by specimen date are shown in Figure
13. Figure 13 shows cases predominate in the North West with no cases detected as of
the 23 February 2021. The supplementary data for figures is available here.
International Epidemiology
The are no cases reported internationally as of the 31 March 2021. GISAID includes data
on sequences available internationally. As of 31 March 2021 1 sequence is listed of VUI21FEB-01
(A.23.1 with E484K) (excluding UK) from Netherlands.
VUI-21FEB-01 (A.23.1 with E484K)
This variant was first identified in Liverpool, UK, derived from a lineage first identified in
Uganda without E484K. The variant was designated VUI-21FEB-01 (A.23.1 with E484K)
on 5 February 2021. It was first detected in the UK in December 2020.
Epidemiological profile
As of 31 March 2021, 78 genomically confirmed cases of VUI-21FEB-01 (A.23.1 with
E484K) have been identified. The majority of these are residents of the North West of
England (Table 12). Confirmed and probable cases by specimen date are shown in Figure
13. Figure 13 shows cases predominate in the North West with no cases detected as of
the 23 February 2021. The supplementary data for figures is available here.
International Epidemiology
The are no cases reported internationally as of the 31 March 2021. GISAID includes data
on sequences available internationally. As of 31 March 2021 1 sequence is listed of VUI21FEB-01
(A.23.1 with E484K) (excluding UK) from Netherlands.

 International Epidemiology
As of 31 March 2021, cases of VUI-21FEB-03 (B.1.525) have been reported in 39
countries or territories.
GISAID includes data on sequences available internationally. As of the 31 March 2021 652
sequences of VUI-21FEB-03 (B.1.525) are listed, from 34 countries or territories excluding
UK
International Epidemiology
As of 31 March 2021, cases of VUI-21FEB-03 (B.1.525) have been reported in 39
countries or territories.
GISAID includes data on sequences available internationally. As of the 31 March 2021 652
sequences of VUI-21FEB-03 (B.1.525) are listed, from 34 countries or territories excluding
UK






