Format of bispecific antibodies (BsAbs)-Hetero H, CrossMab
Virus-like particles (VLP) Platforms for immunogens, vaccines and drug carriers
Antibody-drug Conjugate (ADC): Pre-made ADC benchmark, MOA, Production and QC
Neutralizing antibodies of virus (SARS2, HIV, HBV, Rabies, RSV, Ebola, Influenza)
Immunoglobulin Fc receptors for Fc&Fc Receptor binding assay
ILIBRA-HuEasy Monoclonal antibody (mab) humanization service (fully humanized ab)
Single domain antibody (Nanobody)
SOCAIL MEDIA

CrossMab technology enforces correct light chain association based on the domain crossover of immunoglobulin domains in the Fab region of the bispecific antibody. CrossMab technology allow the generation of various bispecific antibody formats, including bi- (1+1), tri- (2+1) and tetra-(2+2) valent bispecific antibodies, as well as non-Fc tandem antigen-binding fragment (Fab)-based antibodies. These formats may be derived from any existing antibody pair using domain crossover, without the need for the identification of common light chains, post-translational processing/in vitro chemical assembly or the introduction of a set of mutations enforcing correct light chain association. The basis of the CrossMab technology is the crossover of antibody domains within one arm of a bispecific IgG antibody enabling correct chain association, whereas correct heterodimerization of the heavy chains can be achieved by the knob-into-hole technology or charge interactions. This can be achieved by exchange of either the Fab domains (in the CrossMabFab format), or only the variable VH-VL domains (CrossMabVH-VL format) or the constant CH1-CL domains (CrossMabCH1-CL format) within the Fab-fragment (Fig. 1). This class of therapeutics antibodies have novel mechanisms of actions as compared to conventional therapeutic antibodies and have a major impact on the treatment of various diseases, including oncology, infectious diseases, autoimmunity, CNS, and metabolic diseases. Taken together, CrossMab technology has proven to be very useful for the fast and straightforward generation of bispecific antibody formats to tackle novel biological challenges and help to develop novel therapeutic concepts.
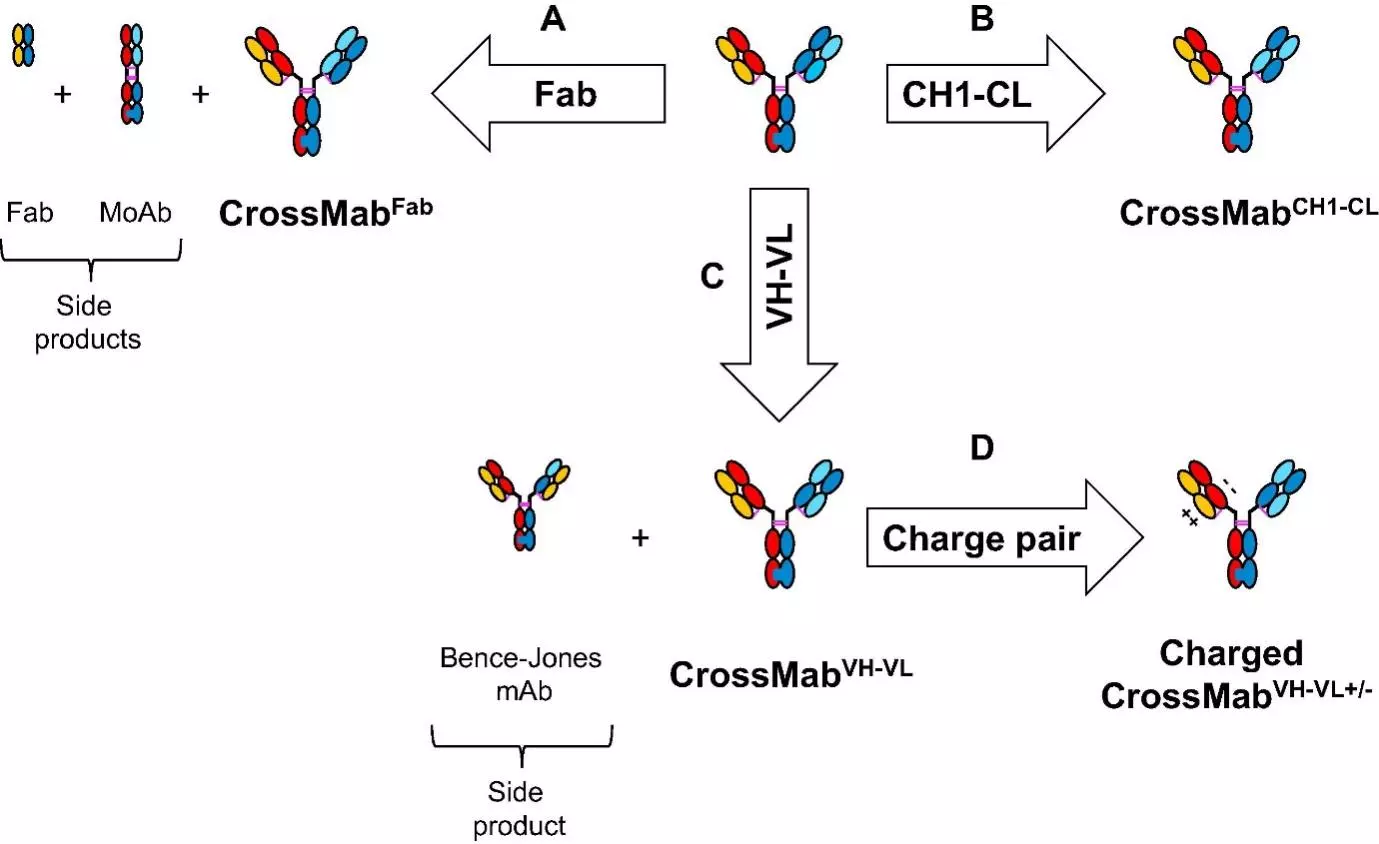
Formats of bispecific antibodies (BsAbs)
Many formats have been developed for BsAb generation as listed in the following table.
| Format | Schematic structure | Description | Example BsAb | Trademark | Company |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tandem VHH | Tandem VHH fragment-based BsAb | N/A | |||
| tandem scFv |  | Tandem ScFv fragment-based BsAb | AMG330 | BiTETM | Amgen |
| Dual-affinity re-targeting antibody |  | Tandem domain-exchanged Fv (can also be used to fuse with Fc domain to create whole Abs) | Flotetuzumab | DARTTM | Macrogenics |
| Diabody |  | dimer of single-chain Fv (scFv) fragment | vixtimotamab | ReSTORETM | Amphivena Therapeutics |
| (scFv)2-Fab |  | a Fab domain and two scFv domains bind | A-337 | ITabTM | Generon/EVIVE Biotech |
| Rat–mouse hybrid IgG |  | Full-size IgG-like half antibodies from two different species | Catumaxomab | TriomabTM | Trion Pharma |
| Hetero heavy chain, Common light chain |  | Hetero heavy chain, Common light chain | Emicizumab | ART-IgTM | Genentech/ Chugai/Roche |
| Controlled Fab arm exchange | 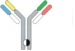 | Recombin the parental half antibodies | JNJ-64007957 | DuobodyTM | Genmab/ Janssen |
| Hetero H, forced HL IgG1 | 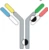 | KIH technology for heterodimerization of 2 distinct H chains, replacing the native disulfide bond in one of the CH1-CL interfaces with an engineered disulfide bond to enhance the cognate of H and L paring | MEDI5752 | DuetMabTM | MedImmune/ AstraZeneca |
| cH IgG1 | 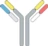 | Identical heavy chains; 2 different light chains: one kappa (κ) and one lambda (λ) | NI-1701 | κλ bodyTM | Novimmune SA |
| Hetero H, CrossMab | 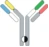 | KIH technology; domain crossover of immunoglobulin domains in the Fab region | Vanucizumab | CrossMabTM | Roche |
| scFv-Fab IgG | 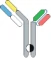 | Fab-Fc; ScFv-Fc | Vibecotamab; M802 | XmabTM (the engineered Fc to enhance the generation of heterodimeric Fc); YBODYTM | Xencor/Amgen; YZYBio |
| VH1-VH2-CH1-Fc1(G1) x VL2-VL1-CL-Fc2(G1) | 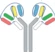 | 2 binding motif in one half antibody | SAR440234 | CODV-IgTM | Sanofi |
| VL1-CL1-VH2-CH2-Fc x VH1-CH1 x VL2-CL2 | 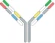 | 2 binding motif in one half antibody | EMB-01 | FIT-IgTM | EPIMAB BIOTHERAPEUTICS |
| VH-1-TCR Cα x VL-1-TCR Cβ; VH-2-CH-2-Fc x VL-2-CL-2 |  | KIH technology; TCR Cα/Cβ is used to substitute the CH1 and CL domain in one arm | WuXibodyTM | WuXi Biologics | |
| C-terminal linker of Fc |  | Link the other molecules at the C-terminal of Fc | APVO442 | ADAPTIR-FLEXTM | Aptevo Therapeutics |
| Fc antigen binding site |  | 2 natural binding sites; 2 additional binding sites in the Fc loop | FS118 | mAb2 | F-star Therapeutics |




