Format of bispecific antibodies (BsAbs)-Hetero H, forced HL IgG1
Virus-like particles (VLP) Platforms for immunogens, vaccines and drug carriers
Antibody-drug Conjugate (ADC): Pre-made ADC benchmark, MOA, Production and QC
Neutralizing antibodies of virus (SARS2, HIV, HBV, Rabies, RSV, Ebola, Influenza)
Immunoglobulin Fc receptors for Fc&Fc Receptor binding assay
ILIBRA-HuEasy Monoclonal antibody (mab) humanization service (fully humanized ab)
Single domain antibody (Nanobody)
SOCAIL MEDIA

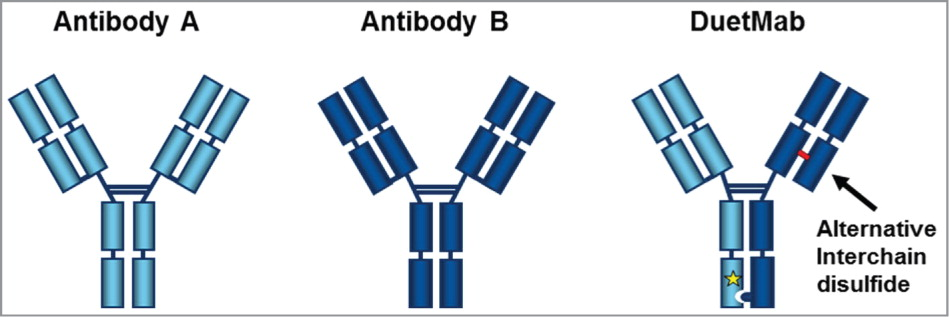
Hetero H, forced HL IgG1/ DuetMab replaces the native disulfide bond in the CH1-CL interface with an engineered disulfide bond (fig. 1). This enhances cognate light chain pairing. Three different positions in the CH1-CL interface are possible candidates for favoring the formation of a novel disulfide bond. An amino acid on the HC and one on the LC is replaced with cysteine in one of the Fab regions. The native disulfide bond on the other Fab region is left intact. It is advantageous that the modifications are in the CH1-CL interface and not in the variable domain, as this could have detrimental effects on antigen binding. Although, engineering in the CH1-CL interface could mean that κ and λ constant light chains would somehow affect the usefulness of this approach. However, it was shown to be compatible to both isotypes (Mazor et al. 2015). DuetMab could be generically applied to bispecific antibodies in development since the approach: (i) does not contain variable domain engineering, (ii) is compatible with both kappa and lambda isotypes and (iii) was able to induce correct heterodimerization.
Formats of bispecific antibodies (BsAbs)
Many formats have been developed for BsAb generation as listed in the following table.
| Format | Schematic structure | Description | Example BsAb | Trademark | Company |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tandem VHH | Tandem VHH fragment-based BsAb | N/A | |||
| tandem scFv |  | Tandem ScFv fragment-based BsAb | AMG330 | BiTETM | Amgen |
| Dual-affinity re-targeting antibody |  | Tandem domain-exchanged Fv (can also be used to fuse with Fc domain to create whole Abs) | Flotetuzumab | DARTTM | Macrogenics |
| Diabody |  | dimer of single-chain Fv (scFv) fragment | vixtimotamab | ReSTORETM | Amphivena Therapeutics |
| (scFv)2-Fab |  | a Fab domain and two scFv domains bind | A-337 | ITabTM | Generon/EVIVE Biotech |
| Rat–mouse hybrid IgG |  | Full-size IgG-like half antibodies from two different species | Catumaxomab | TriomabTM | Trion Pharma |
| Hetero heavy chain, Common light chain |  | Hetero heavy chain, Common light chain | Emicizumab | ART-IgTM | Genentech/ Chugai/Roche |
| Controlled Fab arm exchange | 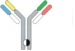 | Recombin the parental half antibodies | JNJ-64007957 | DuobodyTM | Genmab/ Janssen |
| Hetero H, forced HL IgG1 | 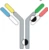 | KIH technology for heterodimerization of 2 distinct H chains, replacing the native disulfide bond in one of the CH1-CL interfaces with an engineered disulfide bond to enhance the cognate of H and L paring | MEDI5752 | DuetMabTM | MedImmune/ AstraZeneca |
| cH IgG1 | 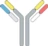 | Identical heavy chains; 2 different light chains: one kappa (κ) and one lambda (λ) | NI-1701 | κλ bodyTM | Novimmune SA |
| Hetero H, CrossMab | 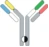 | KIH technology; domain crossover of immunoglobulin domains in the Fab region | Vanucizumab | CrossMabTM | Roche |
| scFv-Fab IgG | 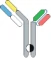 | Fab-Fc; ScFv-Fc | Vibecotamab; M802 | XmabTM (the engineered Fc to enhance the generation of heterodimeric Fc); YBODYTM | Xencor/Amgen; YZYBio |
| VH1-VH2-CH1-Fc1(G1) x VL2-VL1-CL-Fc2(G1) | 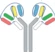 | 2 binding motif in one half antibody | SAR440234 | CODV-IgTM | Sanofi |
| VL1-CL1-VH2-CH2-Fc x VH1-CH1 x VL2-CL2 | 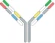 | 2 binding motif in one half antibody | EMB-01 | FIT-IgTM | EPIMAB BIOTHERAPEUTICS |
| VH-1-TCR Cα x VL-1-TCR Cβ; VH-2-CH-2-Fc x VL-2-CL-2 |  | KIH technology; TCR Cα/Cβ is used to substitute the CH1 and CL domain in one arm | WuXibodyTM | WuXi Biologics | |
| C-terminal linker of Fc |  | Link the other molecules at the C-terminal of Fc | APVO442 | ADAPTIR-FLEXTM | Aptevo Therapeutics |
| Fc antigen binding site |  | 2 natural binding sites; 2 additional binding sites in the Fc loop | FS118 | mAb2 | F-star Therapeutics |




