Rat-mouse hybrid IgG
Virus-like particles (VLP) Platforms for immunogens, vaccines and drug carriers
Antibody-drug Conjugate (ADC): Pre-made ADC benchmark, MOA, Production and QC
Neutralizing antibodies of virus (SARS2, HIV, HBV, Rabies, RSV, Ebola, Influenza)
Immunoglobulin Fc receptors for Fc&Fc Receptor binding assay
ILIBRA-HuEasy Monoclonal antibody (mab) humanization service (fully humanized ab)
Single domain antibody (Nanobody)
SOCAIL MEDIA

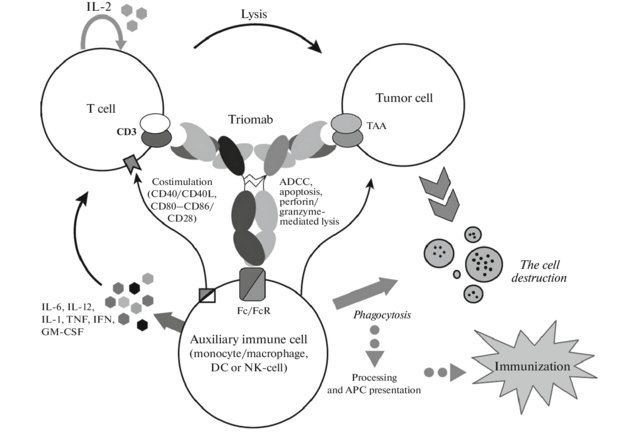
Rat-mouse hybrid IgG is a monoclonal antibody with binding sites for two different antigens, typically CD3 and a tumor antigen, making it a type of bispecific monoclonal antibody. In addition, its intact Fc-part can bind to an fc receptor on accessory cells like conventional monospecific antibodies. The net effect is that this type of drug links T cells (via CD3) and monocytes/macrophages, natural killer cells, dendritic cells or other Fc receptor expressing cells to the tumor cells, leading to their destruction.
At first, monoclonal antibodies against the desired antigens are produced using mouse hybridoma cells. Simultaneously, monoclonal antibodies against another antigen are produced using rat hybridoma cells. These two hybridoma cells are hybridized to produce hybrid-hybridomas or quadromas of hybrid (trifunctional) antibody. The trifunctional antibody is extracted and purified using protein A chromatography.
Trifunctional antibodies eliminate tumor cells by means of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytoxicity and cytotoxic T cell responses with emphasis on CD8 T cells. These trifunctional antibodies also elicit individual anti-tumor immune responses in cancer patients. The principle of trifunctional antibody activity is shown in Fig. 1. Trifunctional antibody activates T cells, and release TNF and IFN-γ cytokines. In addition, FcγR-positive cells are sent to the tumor foci, where they actively produce proinflammatory cytokines IL-6, IL-12, GM-CSF, and DC-CK1. The interaction of T cells and CD14-positive monocytes, activated via Fc/FcR, leads to increased expression of CD83, CD86 and CD40, providing T cells with an additional costimulatory signal from CD40/CD40L or CD80- CD86/CD28, which enhances the therapeutic effect of the antibodies. In such case tumor cells are effectively destroyed not only by direct attack of T cells, but through other mechanisms such as antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, phagocytosis, perforin/granzyme mediated lysis, and induction of apoptosis by activated immune system accessory cells. The resulting necrotic and apoptotic tumor particles are phagocytized, processed, and presented by professional antigen-presenting cells (macrophages, dendritic cells), which is a prerequisite for long-term anticancer immunization.
Formats of bispecific antibodies (BsAbs)
Many formats have been developed for BsAb generation as listed in the following table.
| Format | Schematic structure | Description | Example BsAb | Trademark | Company |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tandem VHH | Tandem VHH fragment-based BsAb | N/A | |||
| tandem scFv | 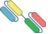 | Tandem ScFv fragment-based BsAb | AMG330 | BiTETM | Amgen |
| Dual-affinity re-targeting antibody |  | Tandem domain-exchanged Fv (can also be used to fuse with Fc domain to create whole Abs) | Flotetuzumab | DARTTM | Macrogenics |
| Diabody |  | dimer of single-chain Fv (scFv) fragment | vixtimotamab | ReSTORETM | Amphivena Therapeutics |
| (scFv)2-Fab |  | a Fab domain and two scFv domains bind | A-337 | ITabTM | Generon/EVIVE Biotech |
| Rat–mouse hybrid IgG |  | Full-size IgG-like half antibodies from two different species | Catumaxomab | TriomabTM | Trion Pharma |
| Hetero heavy chain, Common light chain | 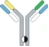 | Hetero heavy chain, Common light chain | Emicizumab | ART-IgTM | Genentech/ Chugai/Roche |
| Controlled Fab arm exchange | 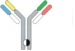 | Recombin the parental half antibodies | JNJ-64007957 | DuobodyTM | Genmab/ Janssen |
| Hetero H, forced HL IgG1 | 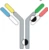 | KIH technology for heterodimerization of 2 distinct H chains, replacing the native disulfide bond in one of the CH1-CL interfaces with an engineered disulfide bond to enhance the cognate of H and L paring | MEDI5752 | DuetMabTM | MedImmune/ AstraZeneca |
| cH IgG1 | 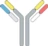 | Identical heavy chains; 2 different light chains: one kappa (κ) and one lambda (λ) | NI-1701 | κλ bodyTM | Novimmune SA |
| Hetero H, CrossMab | 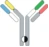 | KIH technology; domain crossover of immunoglobulin domains in the Fab region | Vanucizumab | CrossMabTM | Roche |
| scFv-Fab IgG | 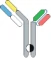 | Fab-Fc; ScFv-Fc | Vibecotamab; M802 | XmabTM (the engineered Fc to enhance the generation of heterodimeric Fc); YBODYTM | Xencor/Amgen; YZYBio |
| VH1-VH2-CH1-Fc1(G1) x VL2-VL1-CL-Fc2(G1) | 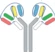 | 2 binding motif in one half antibody | SAR440234 | CODV-IgTM | Sanofi |
| VL1-CL1-VH2-CH2-Fc x VH1-CH1 x VL2-CL2 | 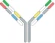 | 2 binding motif in one half antibody | EMB-01 | FIT-IgTM | EPIMAB BIOTHERAPEUTICS |
| VH-1-TCR Cα x VL-1-TCR Cβ; VH-2-CH-2-Fc x VL-2-CL-2 |  | KIH technology; TCR Cα/Cβ is used to substitute the CH1 and CL domain in one arm | WuXibodyTM | WuXi Biologics | |
| C-terminal linker of Fc |  | Link the other molecules at the C-terminal of Fc | APVO442 | ADAPTIR-FLEXTM | Aptevo Therapeutics |
| Fc antigen binding site |  | 2 natural binding sites; 2 additional binding sites in the Fc loop | FS118 | mAb2 | F-star Therapeutics |




