Format of bispecific antibodies (BsAbs)-Tandem scFv
Virus-like particles (VLP) Platforms for immunogens, vaccines and drug carriers
Antibody-drug Conjugate (ADC): Pre-made ADC benchmark, MOA, Production and QC
Neutralizing antibodies of virus (SARS2, HIV, HBV, Rabies, RSV, Ebola, Influenza)
Immunoglobulin Fc receptors for Fc&Fc Receptor binding assay
ILIBRA-HuEasy Monoclonal antibody (mab) humanization service (fully humanized ab)
Single domain antibody (Nanobody)
SOCAIL MEDIA

A tandem scFv links two or more scFvs with the helical peptide linkers in the orientation NH2–VL1–VH1–(linker–VL2–VH2)n–COOH, resulting in a single chain bivalent and bi-specific molecule encoded by a single gene (Figure 2). Tandem scFv can be used to target two different antigens on two different cells, two different antigens on the same cell, or two different epitopes on the same antigen with increased avidity.
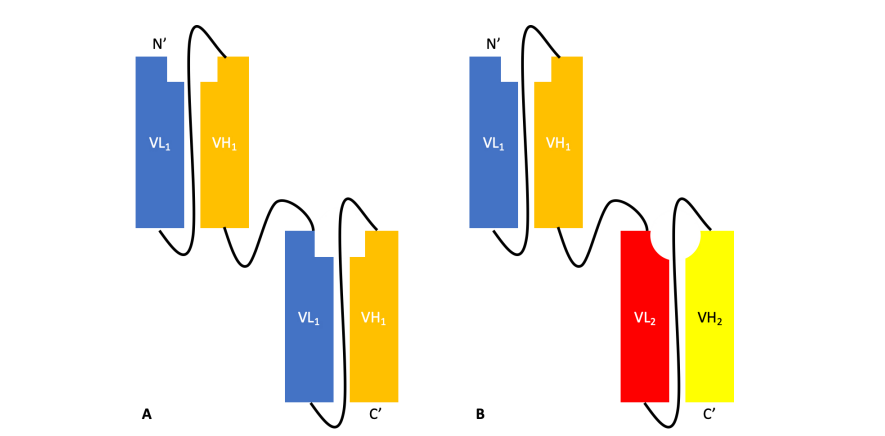
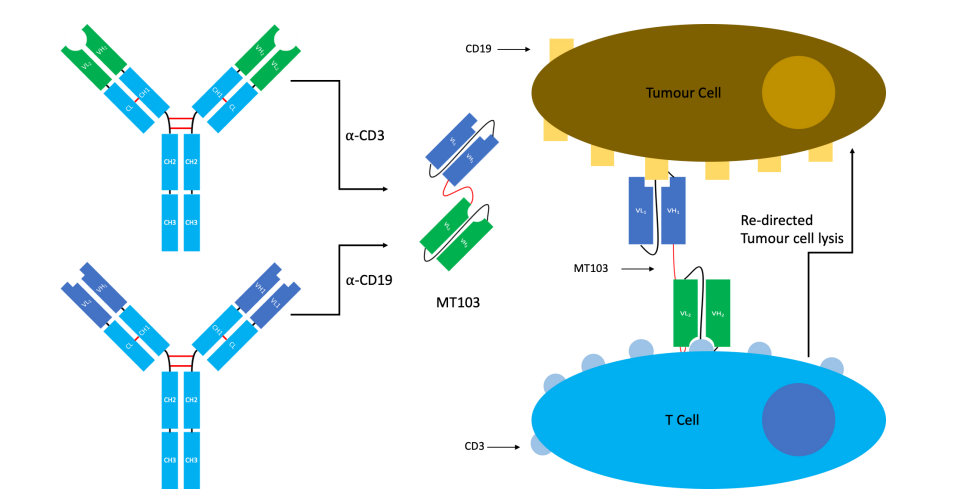
Bispecific T-cell engagers (BiTE) are a type of tandem scFv used to redirect cytotoxic T-cells to tumors. The induced response is highly selective against the target tumor cells (Figure 3). It contains two antigen binding sites. The first is focused towards a tumor antigen, whereas the second is focused towards the T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling complex CD3. Simultaneous binding of the BiTE to CD3 and the tumor antigen evades pMHC restriction and encourage T-cell activation and cytokine production towards the tumor-directed cytotoxic response, and the activation of other host immune responses. Bispecific T-cell engagers has been used to treat the non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and Philadelphia chromosome negative acute lymphoblastic. In addition, Bispecific killer cell engagers (BiKEs) and trispecific killer cell engagers (TriKEs) are bi- or trispecific tandem scFvs has been developed to redirect natural killer (NK) cells via an anti-CD16 scFv.
Formats of bispecific antibodies (BsAbs)
Many formats have been developed for BsAb generation as listed in the following table.
| Format | Schematic structure | Description | Example BsAb | Trademark | Company |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tandem VHH | Tandem VHH fragment-based BsAb | N/A | |||
| tandem scFv | 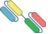 | Tandem ScFv fragment-based BsAb | AMG330 | BiTETM | Amgen |
| Dual-affinity re-targeting antibody |  | Tandem domain-exchanged Fv (can also be used to fuse with Fc domain to create whole Abs) | Flotetuzumab | DARTTM | Macrogenics |
| Diabody |  | dimer of single-chain Fv (scFv) fragment | vixtimotamab | ReSTORETM | Amphivena Therapeutics |
| (scFv)2-Fab |  | a Fab domain and two scFv domains bind | A-337 | ITabTM | Generon/EVIVE Biotech |
| Rat–mouse hybrid IgG |  | Full-size IgG-like half antibodies from two different species | Catumaxomab | TriomabTM | Trion Pharma |
| Hetero heavy chain, Common light chain | 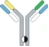 | Hetero heavy chain, Common light chain | Emicizumab | ART-IgTM | Genentech/ Chugai/Roche |
| Controlled Fab arm exchange | 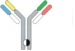 | Recombin the parental half antibodies | JNJ-64007957 | DuobodyTM | Genmab/ Janssen |
| Hetero H, forced HL IgG1 | 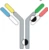 | KIH technology for heterodimerization of 2 distinct H chains, replacing the native disulfide bond in one of the CH1-CL interfaces with an engineered disulfide bond to enhance the cognate of H and L paring | MEDI5752 | DuetMabTM | MedImmune/ AstraZeneca |
| cH IgG1 | 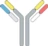 | Identical heavy chains; 2 different light chains: one kappa (κ) and one lambda (λ) | NI-1701 | κλ bodyTM | Novimmune SA |
| Hetero H, CrossMab | 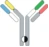 | KIH technology; domain crossover of immunoglobulin domains in the Fab region | Vanucizumab | CrossMabTM | Roche |
| scFv-Fab IgG | 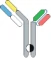 | Fab-Fc; ScFv-Fc | Vibecotamab; M802 | XmabTM (the engineered Fc to enhance the generation of heterodimeric Fc); YBODYTM | Xencor/Amgen; YZYBio |
| VH1-VH2-CH1-Fc1(G1) x VL2-VL1-CL-Fc2(G1) | 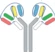 | 2 binding motif in one half antibody | SAR440234 | CODV-IgTM | Sanofi |
| VL1-CL1-VH2-CH2-Fc x VH1-CH1 x VL2-CL2 | 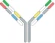 | 2 binding motif in one half antibody | EMB-01 | FIT-IgTM | EPIMAB BIOTHERAPEUTICS |
| VH-1-TCR Cα x VL-1-TCR Cβ; VH-2-CH-2-Fc x VL-2-CL-2 |  | KIH technology; TCR Cα/Cβ is used to substitute the CH1 and CL domain in one arm | WuXibodyTM | WuXi Biologics | |
| C-terminal linker of Fc |  | Link the other molecules at the C-terminal of Fc | APVO442 | ADAPTIR-FLEXTM | Aptevo Therapeutics |
| Fc antigen binding site |  | 2 natural binding sites; 2 additional binding sites in the Fc loop | FS118 | mAb2 | F-star Therapeutics |




